Is External Drive Shucking Still Worth It?
As long as there have been ready-made USB external hard drives, there has been shucking. Hard Drive Shucking (and in recent years, even SSD shucking) is the process of purchasing an external HDD/SSD enclosure, such as WD My Book or Seagate Backup Plus drive, and then cracking open the casing to get the drive inside. Now, on the face of it, this might seem a bit daft. After all, you can definitely still buy bare/internal HDDs on there own. Why would you go the ‘scenic route’ and purchase a lovely well designed external drive, only to crack the casing open, possibly undermining your warranty, when you can just simply buy the bare drive online and not have to get your hands dirty? Well, the reality of shucking is actually a great deal more nuanced and there are actually several more advantages to HDD/SSD shucking above and beyond the price point! So, today I want to discuss the three reasons why you might want to consider shucking a hard drive or SSD (as well as three reasons why you might want to give it a miss and buy an internal drive at retail). But first, we need to touch on an important point – how is it possible that a hard drive or SSD inside an official enclosure can possibly arrive at a lower price than buying the drive on it’s own?
Note – We made a YouTube video version of this article HERE
How is it possible for an HDD/SSD in a Case to be cheaper than a Bare Drive on its own?

It’s a good question! Logically, an external 10TB HDD USB or Thunderbolt enclosure should NOT cost less than the 10TB drive on its own, right? However, in reality, there are quite a few reasons why they can sometimes be cheaper. Notwithstanding that an external hard drive might be on some kind of special promotional offer (Black Friday, Prime Day, etc), here are a handful of reasons that an external HDD can cost less than the HDD on it’s own:
- HDDs and SSDs that are used in external USB drives are allocated in bulk and, unlike bare HDD/SSDs that are distributed a little more fluidly by both manufacturers and distribution, the brand (WD, Seagate, Toshiba, etc) have to effectively remove a % of the available stock of drives for use in the external enclosures. This means that it removes them from the more dynamic sale/demand price changes that effect fluid bare HDD/SSD stock levels. For example, if you have 5000 x WD Ultrastar 10TBs , and 2500 of them are in enclosures and 2500 of them are sold as bare drives, the 2500 bare drives are going to rise and fall in popularity and are often purchased in bulk by businesses. Whereas the 2500x external HDD enclosures are subject to the demands of external HDDs (which is arguably more predictable and steady, as well as purchased one or two at a time at most)
- External exclosure drives (such as the WD My Book, Passport, Seagate Backup Plus, Toshiba External) are not subject to the same durability requirements that a bare drive might be subject to. This can often be down to the enclosure capping performance to USB 5Gb/s or in a casing that has it’s own throttling/bottleneck out of necessity such as a docking station. This means that a 10TB bard drive and a 10TB inside an enclosure might not ensure the same workload over a 3-5yr period. This results in the brand not needing to use such ensuring drives or even commit to a single HDD in a series of external enclosure in it’s sales lifetime – swapping out the drive as stock levels/procurement allows
- Some external drives use specific OEM drives to meet a price point. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) drives can often be a completely unique drive that cannot be purchased at retail at all. This can simply be for reasons of portfolio clarity, but can also be because the OEM drive is suitable for external storage but less so for a RAID or as an Operating System drive.
So, thanks to one or more of the above factors, it is actually quite common to find an external USB drive arrive at a lower price point than the same drive that is inside on it’s own. Let’s go through the good and the bad news though.
Reasons You SHOULD Shuck Hard Drives and SSDs
So, let’s start positive! Here are the reasons you should consider shucking a hard drive or SSD, instead of purchasing the bare drive at retail!

Save Money, Free Enclosure and Free Software!
Now, the statement “Shucking HDDs will save you $$$” might seem a bit obvious, but the actual details of the savings AND the gains is often even better than you might think! First up, as detailed above, there is the fact that the HDDs inside the external USB/Thunderbolt enclosures are outside of the sales/demand factors of traditional bare drives, which can mean that you can get a bargain. However, it gets even better. For a start, alot of the more modern HDD/SSD external drive enclosures for 3.5″ HDDs are actually quite high quality and in a more modular design, so you can actually still reuse the SATA enclosure after you have removed the drive. So, not only have you now got your HDD for cheaper than buying it on it’s own, but you also have a free storage enclosure to chuck an older drive into (perhaps one that yu are swapping out for your newer and bigger HDD/SSD). But the gains do not stop there! On top of this, there is the fact that alot of more modern external enclosures are sold with free backup and/or cloud storage software included (many with a free portion of cloud storage too) as the sales focus on external drives have shifted more towards their use as a backup device more than anything. Software such as Acronis, Drive subscriptions, EaseUS, Backupper and Veritas will often be found bundled with your USB/Thunderbolt external drive. So, although the benefits of saving money on HDD or SSD when shucking always takes center stage, it’s worth remembering that the actual value for money and what you end up with can be even better!
Note – 2.5″ HDD/SSD enclosures are often designed in a much more sealed and specific manner, so this can make their re-use after removing the drive inside a slimmer chance, But more on that later…

Rare, OEM only or Hard to Find HDDs Are More Widely Available
This is a factor that is often overlooked, but there are a decent % of quite rare HDDs and SSDs that are ONLY available these days in external drives. Sometimes it is because the drive in question is needed to replace a drive in an old RAID enabled NAS/DAS system and you want to match the existing HDD/SSDs in the array but those drives have been replaced by a newer and possibly unsuitable model. These can often include the oddest capacities, such as 1.5TB, 3TB or 5TB (as well as SSHD Hybrid drives), and this is especially true in the case of 2.5″ drives! This also extents to a number of ht more obscure WD Ultrastar or Seagate EXOS drives that see quite regular refreshes in their portfolios by the brands in question. When this happens, the remaining bare drive stock will more often than not end up in external enclosures, end up either completely removed from sale or end up at painfully small stock availability and increased in price. These price increases rarely affect the external drives though, as WD/Seagate/Toshiba VERY rarely detail the drives they include in the external USB/Thunderbolt drives. Finally, you have specific OEM drives that are not available for purchase anywhere online, but you might want them to replace/upgrade an existing OEM drive in your laptop, tablet or other portable systems. These can include specific-sized 7mm 2.5″ drives or 2260 or 2242 m.2 media that is simply no longer available or never was commercially as a bare drive. If you are looking for a lesser or rare drive, shucking might well be your only option!
Unleash the REAL Performance of the Internal Drive
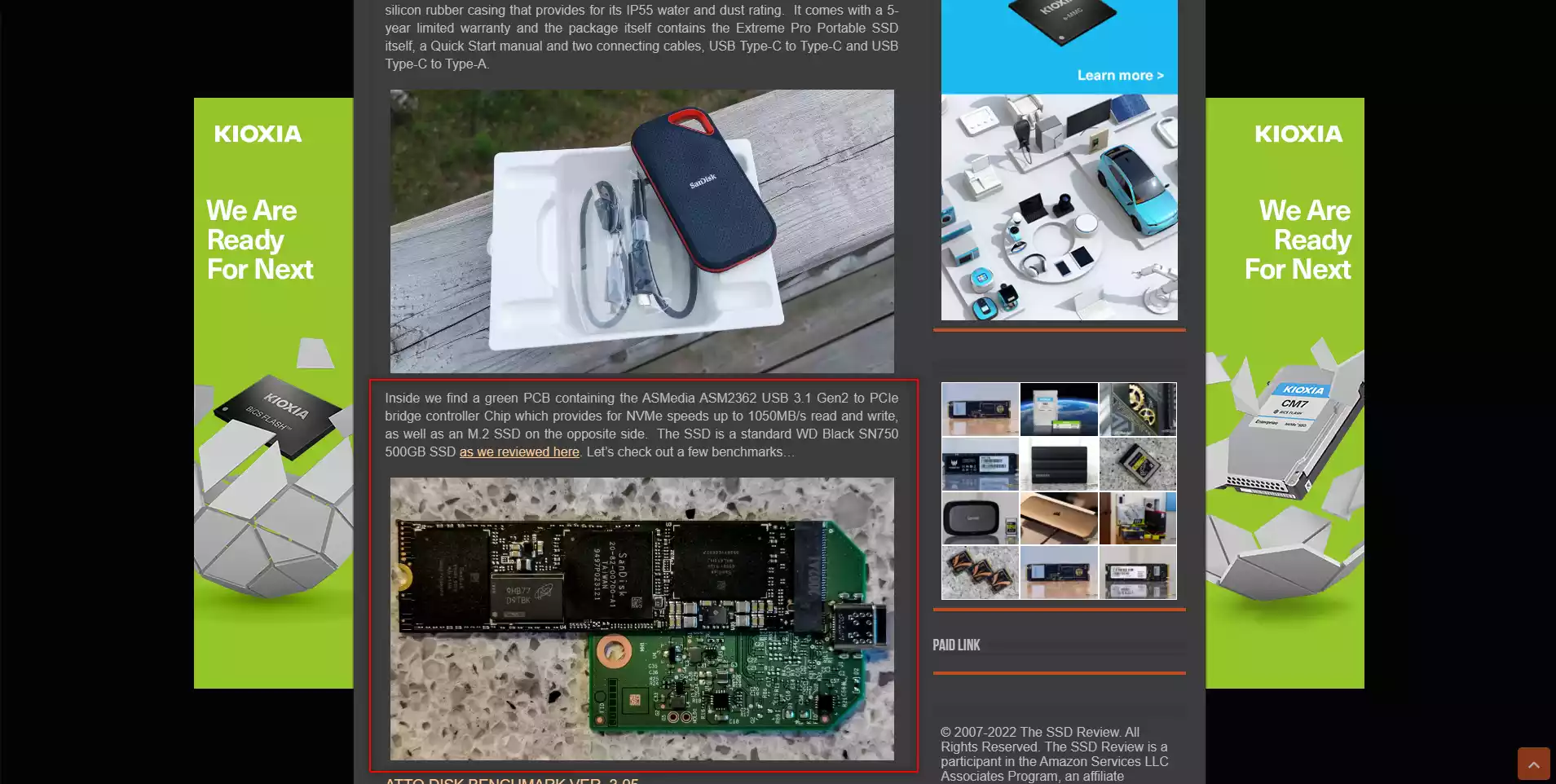
This is MASSIVELY overlooked and a little more focused on SSDs, but for many/all of the reasons detailed above it is often the case that the SSD inside the USB enclosures that you find in the Sandisk/WD/Seagate/Toshiba ranges are being massively bottlenecked by the external interface of the drive. Now, this isn’t a massive surprise really (at first). An external USB 3.2 Gen 1 drive (so, 5Gb/s or 550MB/s) might have one or two SSDs inside that because of the shared bandwidth up/down of an external rive might well throttle the transfer/IOPS of the drive inside. HOWEVER, where it gets REALLY interesting is in the case of USB 3.2 Gen 2 External drives. In the last few years, we have seen USB change it’s name (sigh, USB 3.0, became USB 3.1, which became USB 3.1 Gen 1, and on and on). but the ones you need to focus on are USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10Gb/s or 1,000MB/s) and USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 (20Gb/s or 2,000MB/s). As fast as these sound, it gets better. As in order for the drive inside to saturate this connection, it needs to use an m.2 NVMe SSD drive. Now, modern PCIe Gen 3 NVMes can comfortably hit 3,000-3,4000MB/s transfer speeds and IOPS in the hundreds of thousands (less so with QLC SSDSs, but they will exceed 2,500MB/s more often than not). Now, SSD manufacturers do not go out of their way to produce capped performance SSDs specifically for external enclosures. Aside from the hassle of intentionally producing lower-speed drives (as well as lower-density NAND + lower-tier controllers), it would just overcomplicate production runs. So, more often than not, the brand will use one of their existing range of NVMes and put them inside the USB 3.2 enclosure. The result is that you will often find much, MUCH more expensive drives (as well as much faster drives) inside these enclosures. One great example is from below from TheSSDReview, where the 1,000MB/s Sandisk Extreme Pro for £89 has a WD Black SN750 $109 3,100MB/s SSD inside! This is ALOT more common than you might think and is often at its worst (or best?) in the USB 3.2 Gen 2 and USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 drives.
Reasons You SHOULD NOT Shuck Hard Drives and SSDs
However, as mentioned, hard drive and SSD shucking NOT for everyone! As good as the above three reasons sound, here are three reasons why you might want to give HDD/SSD shucking a miss!
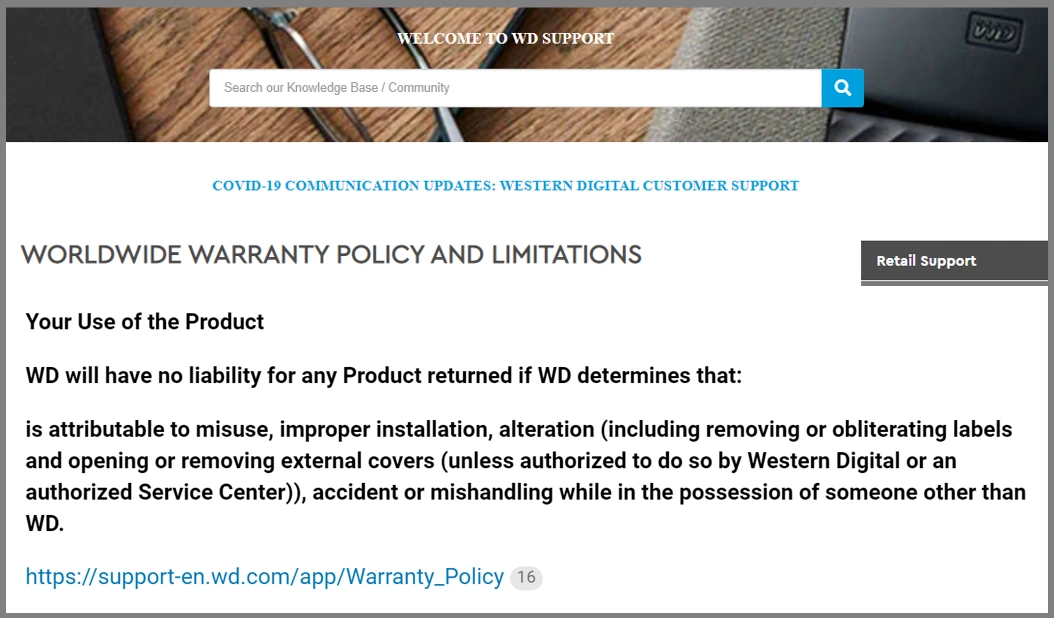
Warranty & Support will be practically ZERO!
This might sound obvious, but seriously – do NOT rely on or depend on your warranty/support if you shuck an HDD or SSD! All of the storage media manufacturers keep a tight record on the serial numbers of drives that are used for external enclosures and although the bare drive might of had a 3-5yr warranty and the external HDD also had a 3-5yr warranty – removing the drive from that enclosure (often breaking intentionally seals that are put in place by the manufacturer) can more often than not completely END any support they will provide. Even if you manage to shuck an HDD or SSD from an enclosure cleanly, the drive logs and S.M.A.R.T on the drive will likely give you away if you submit the drive for an RMA. Brands provide external drives with support/warranty/guarantees that are specific to that kind of end-use – i.e the warranty/fair-use of an external enclosure does not include cracking it open and using it in a RAID or as an OS drive.
Now, I say that support is ‘practically zero’, because SOMETIMES there is wiggle-room. Eg, you might be able to pursue the replacement/warranty via the e-retailer (eTailer?) that you purchased though, as opposed to going directly to the manufacturer for your RMA/Warranty claim. Now, you might be on slightly shakey moral/legal ground here, as that eShop will still need to conduct the warranty internally with the brand and could easily hold off on a replacement/refund until the brand confirms it’s eligibility, but nevertheless, that does still mean that there is still a sliver of a chance – though it’s hardly concrete!
Soldered and Fixed Interfaces by Manufacturers
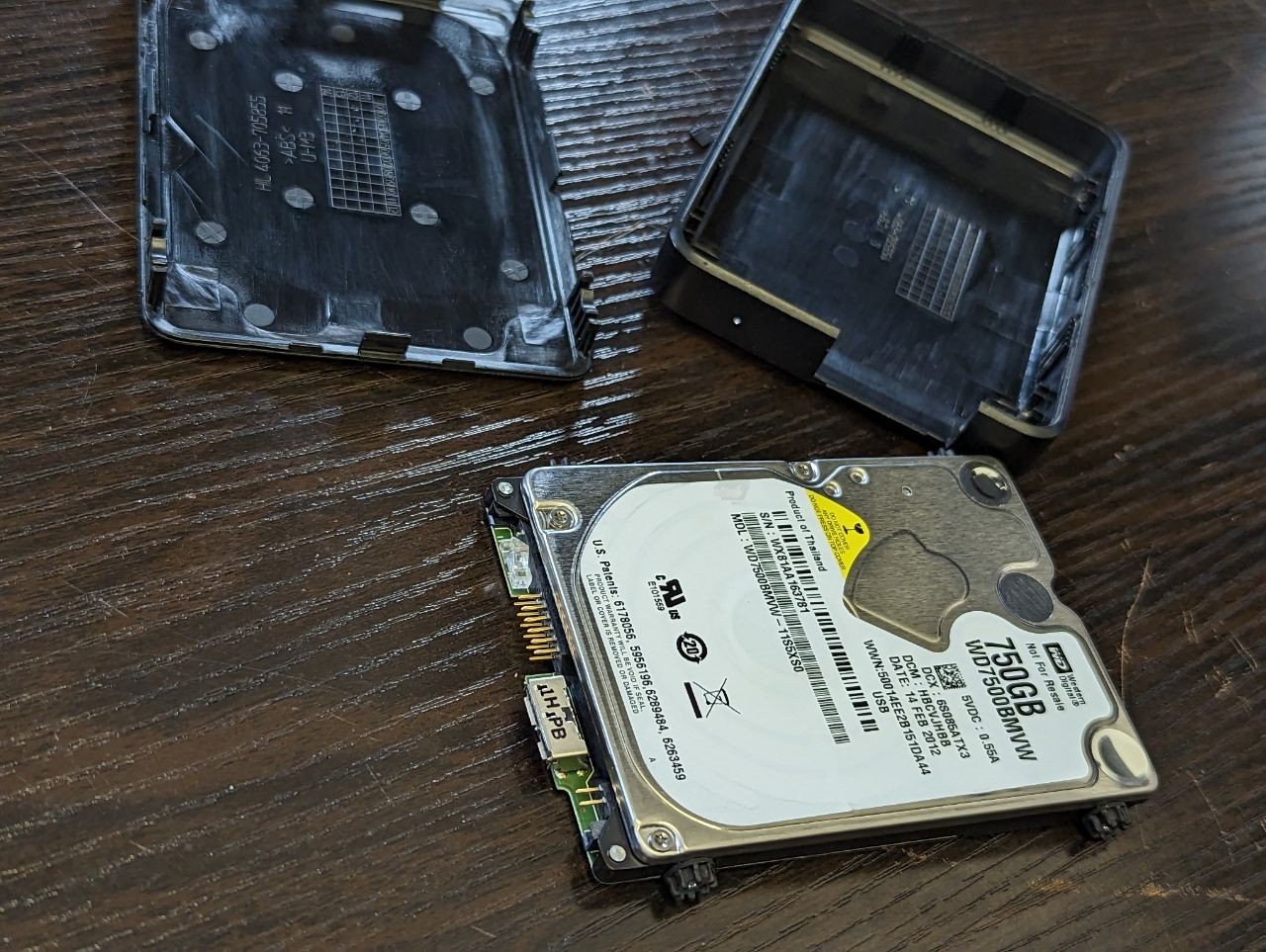
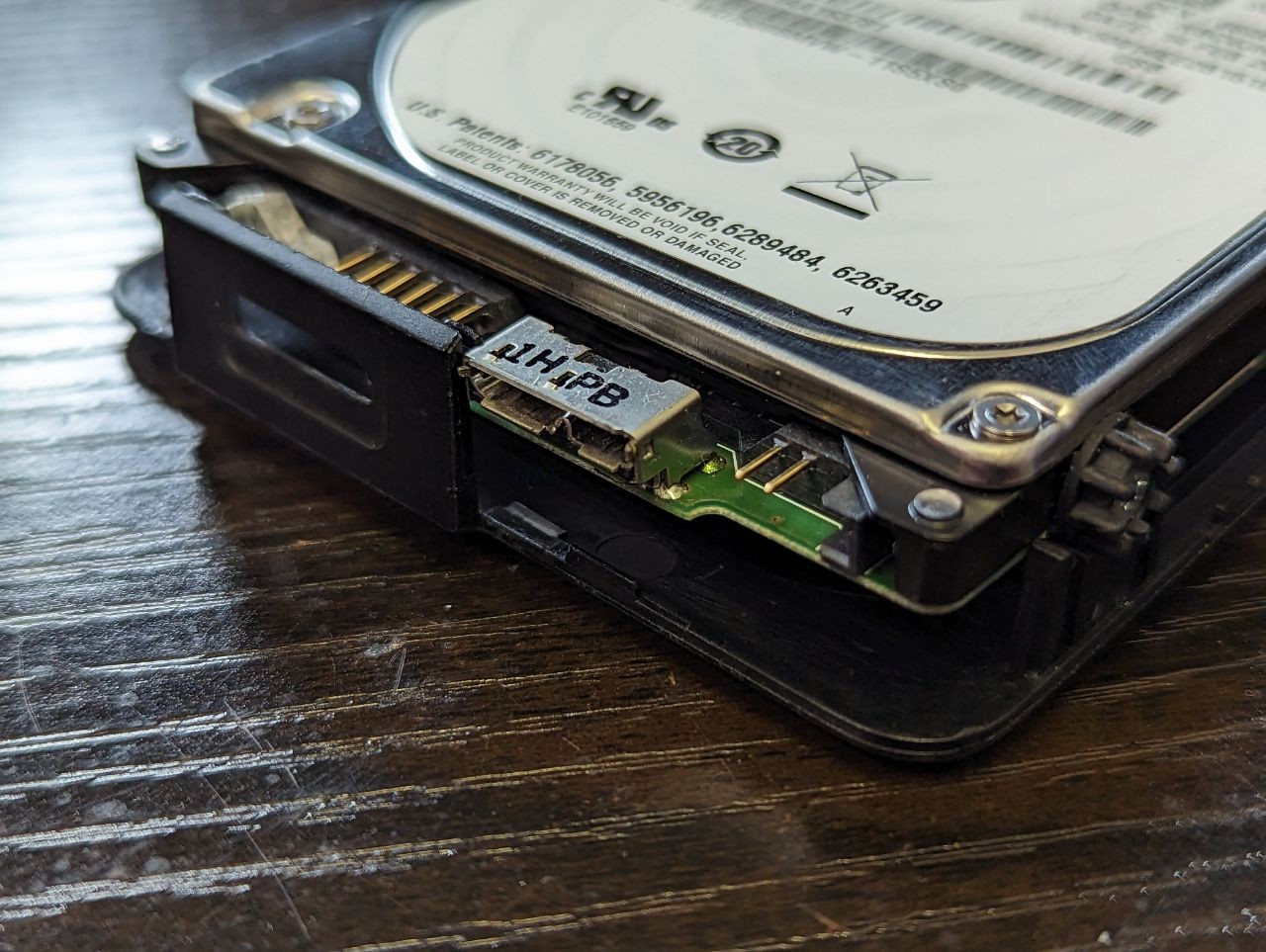
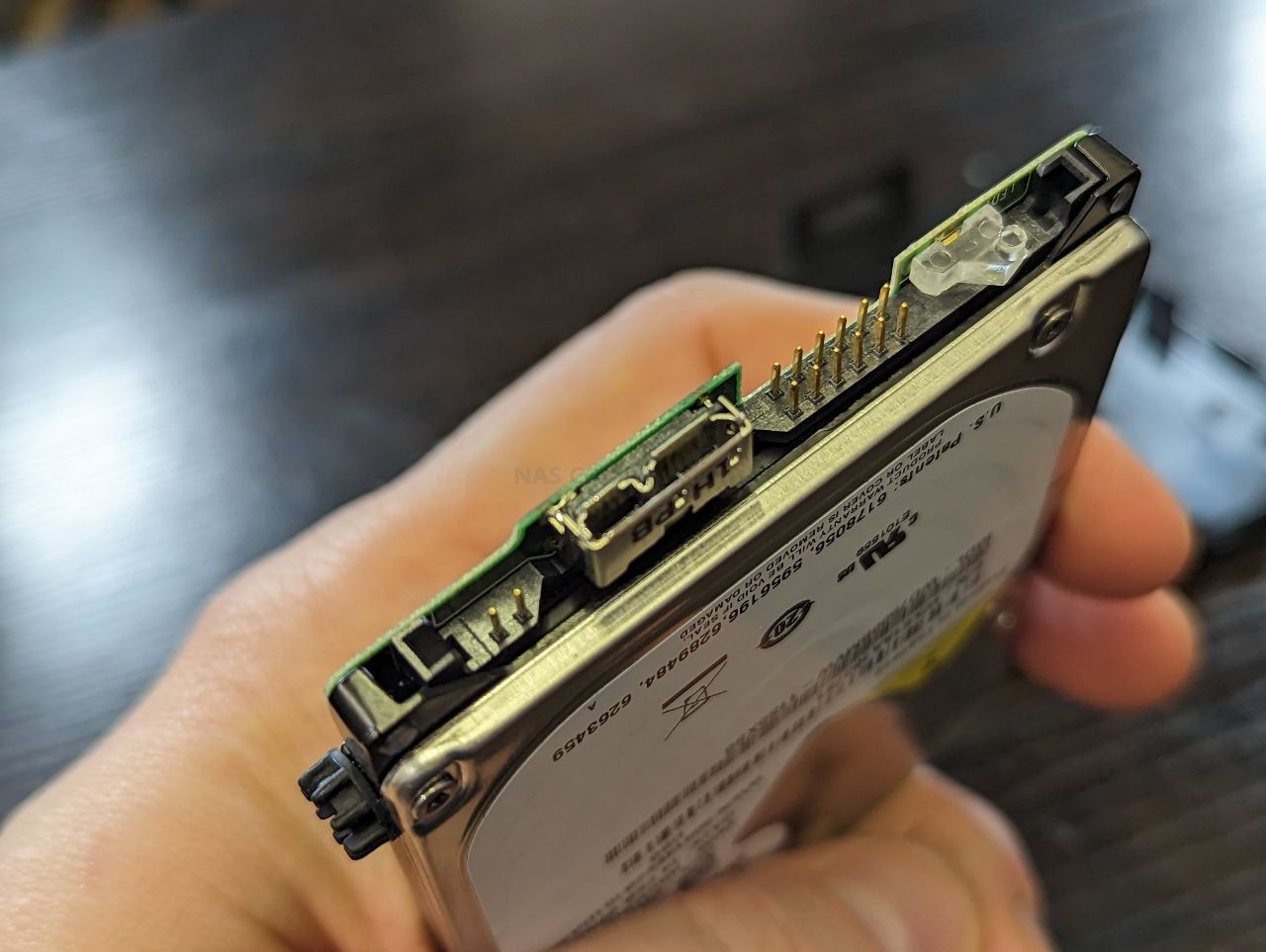
Now one area in which brands have tried to stamp out HDD/SSD shucking (as it can often result in a loss of revenue – those poor, poor multi-billion dollar companies…) is adapting the drive inside the USB external drive enclosure to ONLY be usable inside this casing. Despite drive media changing exponentially in the last 2-3 decades, most internal drive media can be broken down now to just three popular interfaces – SATA, NVMe and mSATA.There are others (eg SAS, U.2, etc), but there are rarely used in external drives that you will consider for shucking. However, despite the drive inside a WD My Book, My Passport or Toshiba Canvio being nearly identical to a regular barebone internal drive, it MIGHT arrive with it’s interface partially or FULLY replaced by a SATA-to-USB bridge board that is soldered to the drive itself. Sometimes, this bridge is just clipped on and/or screwed ot the drive and can be removed. However, sometimes (as seen in the example below with a WD My Passport from 2019), the interface a USB 3.2 Gen 1 Type-B Micro drive will specifically replace the usual SATA interface! Be aware!
Internal HDDs and SSD Choices are Subject to Change
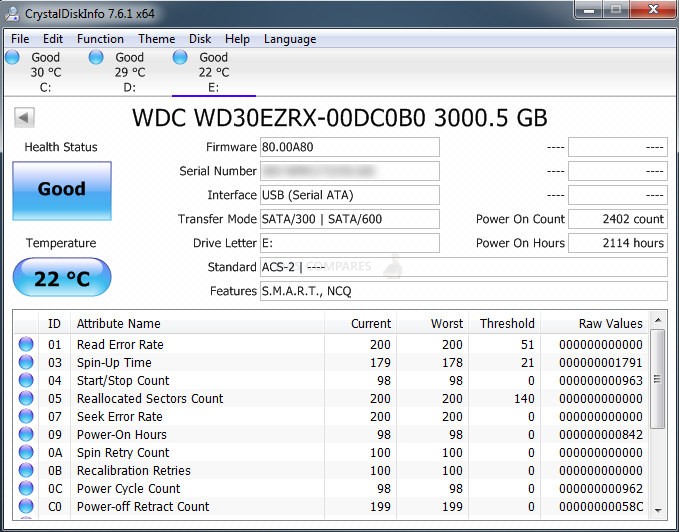
More often than not, THIS is the reason that HDD and SSD shucking of external drives has never been especially dependable as a long-term solution. The hard drives or solid-state drives that the store media brands allocate to their external drive ranges are subject to change! Now, because media brands rarely publically disclose the HDD/SSD inside the enclosure in data sheets (seriously, I have only seem them highlight the drive inside once in 20 years of my career), it means you are hugely dependent of public forums, reviews and benchmarking tools by 3rd parties (eg review sites, Reddit, even Facebook groups) to share which drives are inside external USB drives. Understandably, most consumers are hesitant to crack open an external drive to share the knowledge of a drive inside, potentially invalidating their warranty. HDD and SSD review sites will often make a point of opening up an external drive when reviewing or using tools such as CrystalDiskMark to access the drive and show the drive model ID inside, which is good.
However, because the likes of WD, Seagate and Toshiba can swap allocated drives at production at any time (based on demand and availability), the information detailed online of the contents of an external USB/Thunderbolt enclosure has the potential to be invalid/outdated as time passes – and that isn’t factoring in the potential that those same SSD media manufacturers use more than one drive in a series at once. They just need to use a drive that fits the external drive use case scenario, which as we have detailed above, is much less potent than many bare drives. A 2022 review might well say that the drive inside your WD My Book is an Ultrastar HC310 or WD Black 10TB, but buying it in 2023 might end up with you buying a plain, bog standard WD Blue 10TB. Buyer Beware!
How to Check Which Drive is Inside a USB/Thunderbolt External Enclosure WithoutOpning It?
If you have purchased an external drive (e.g WD My Book, WD My Passport, Sandisk Extreme, Toshiba Canvio or Seagate Backup Plus) and want to check which HDD/SSD is inside WITHOUT physically opening the case (so you have the open to send back immediately if it’s unsuitable), I strongly recommend using the tool CrystalDiskInfo, which can be found HERE. Although there are different tools in the CrystalDisk toolkit, the Info tool is the one you want! In most cases, you will not even need to initialize the drive formally (eg create a usable volume with ‘Disk Management > Select Drive > Create Volume > Drive Letter > Format > etc), as it should appear as an available drive regardless, even over USB.Just ensure that 1) you have the drive connected before you run the CrystalDiskInfo application and 2) That the external drive is connected when booting the system (not ecessential, but can make a difference on some drives depending on the interface in question).
How To Choose The BEST Value Hard Drive And Best Price Per TB – Get It Right, FIRST TIME!
Below you will find our automatic hard drive price per TB/GB tool, designed to crawl many, MANY different eShops and divide their cost between the available storage. This allows us to rank/list these drives by the largest amount of terabytes youwill get for your money. This list includes popular hard drive manufacturers, such as Seagate, WD and Toshiba, allowing you to ensure that you are getting excellent value for money on your storage, as well as only choosing the most reputable HDD makers in the world. Before you head down there though, take a moment to quick familiarize yourself with a few key factors that will aid you in understanding how to understand what separates one HDD from another.
Click Below to Use the Best Price per TB Chart (Updated Daily)
How to calculate price per GB / TB?
📧 SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER 🔔 This description contains links to Amazon. These links will take you to some of the products mentioned in today's content. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Visit the NASCompares Deal Finder to find the best place to buy this device in your region, based on Service, Support and Reputation - Just Search for your NAS Drive in the Box Below
🔒 Join Inner Circle
Get an alert every time something gets added to this specific article!
Need Advice on Data Storage from an Expert?
Finally, for free advice about your setup, just leave a message in the comments below here at NASCompares.com and we will get back to you.
 Need Help?
Where possible (and where appropriate) please provide as much information about your requirements, as then I can arrange the best answer and solution to your needs. Do not worry about your e-mail address being required, it will NOT be used in a mailing list and will NOT be used in any way other than to respond to your enquiry.
Need Help?
Where possible (and where appropriate) please provide as much information about your requirements, as then I can arrange the best answer and solution to your needs. Do not worry about your e-mail address being required, it will NOT be used in a mailing list and will NOT be used in any way other than to respond to your enquiry.
TRY CHAT
Terms and Conditions


Synology FS200T NAS is STILL COMING... But... WHY?
Gl.iNet vs UniFi Travel Routers - Which Should You Buy?
UnifyDrive UP6 Mobile NAS Review
UniFi Travel Router Tests - Aeroplane Sharing, WiFi Portals, Power Draw, Heat and More
UGREEN iDX6011 Pro NAS Review
Beelink ME PRO NAS Review
Access content via Patreon or KO-FI
Discover more from NAS Compares
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.











Thumbs up for the orangized disorganized shelving, I bet this guy knows where everything is
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’m very new to this, and will start my journey with 3x2TB drives. This will mainly be used as a replacement for Google Photos. I’ll set it up so I have 2TB parity-data and 4TB storage – then we’ll see how it holds up in the future.
I’m using my old gaming PC as a NAS, which surprisingly have 6x SATA interfaces
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
the answer to the question is it does not matter, back it up is what you need to do!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
????????????????????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Long term power usage starts to add up when you consider the drives running 24/7/365 for the next 4 or 5 years at least. I’m looking at replacing my ageing 10 drive 8/12 TB Unraid server with 20 or even 24TB drives and newer hardware that will use less power at idle. A huge setup cost, and that will allow me to use my existing setup as a backup system that powers up occasionally and does a backup of the new server. I’m looking at something with better reliably and a 5+ year minimum lifespan, and my existing unraid server is starting to show its age in terms of power use and reliability.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
at the end of the day it depends on how much you are storing. some will need 18 TB * 8 or whatever.
also: notepad instead of spreadsheet? ????you could’ve normalized for example for 72 TB (18 tb * 4) 3:30
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
2+2+1+1 tb nvme/ssd drives w my desktop for gaming(ofcourse i would have loved haing only 2*4tb but price was about 1/3 w 2tb+1tb drives and w discounts at the moment of purchase i could even buy ram for my previous desktop+ a few cables(even a few bucks left after this last year)
So why are bigger drives more expensive per 1tb vs samller ones? its more materias n work one would think or is the smaller just so much worse in quality or something?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More drives means more frequent failures. Less drives means more impact of each failure. This can be compared by doing calculations using the announced MTBF, but some models don’t meet their official MTBF.
Larger drives tend to have better performances (higher density means less head movements). The way to know which is faster would be to actually measure both configurations.
One either presents results for specific configurations, which does not help many people, or is bound to end with an “it’s complicated” conclusion. At the end, people choose one or the other on personal preferences and selection criteria. Is consumption or noise important to a YouTuber with a separate server room?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
2 years on this is what i can tell you this. big drives become small drives in the future. thank goodness i went for 18tb drives, bought another one today and just expanded my capacity by 16.4 tb, 2 bays left open and next year i might add yet another 18tb drive, if i had gone for small drives i would need a huge storage bay with 20 hdd, so go big as soon it will be small, 18tb is no longer large in a world of 36 tb drives. capacity is the only reason for hdd use, otherwise go ssd. yes it is expensive and yes the only way to sleep at night is to go raid 6 with large drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
28tb. I’m waiting to see what return-stats are like. The Seagate 20s are still HIGH.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Go for a home server. Put an left over motherboard, CPU, memory, and PSU in a PC case with a LSI HBA card (hopefully a 16 drive card) and run UNRAID… then you can just put whatever you want (no need to match drives since UNRAID allows for any configuration [SATA HDD, SATA SSD, M.2, U.2, NVMe, USB, SAS, whatever you can connect to your machine] you want (no need to match drive capacities)) in there and as many as you want and add another LSI card as you grow insanely large. Plus you’ll have parity drive redundancy, cache drives (if you want them), add on PCI cards if you want, run dockers, run plugins, run VMs, LAN-wide VPN, and a ton of stuff.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
the clicking in the video’s cuts also is some annoying noise
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
At a certain storage capacity, smaller becomes a relative term.
I would not want to build by 60+ TB array from 4-8 TB drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Bigger hdd but never ever EVER a Nas, I simply build a server with filters ventilation etc.
Way better in terms of performances and everyday use and repairs.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
or using UnRaid, you can mix old HDDs for example, thats a bit cheaper than qnap/synology nas, if you got an old pc maybe laying around…
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
If I could set it up as I imagine, I’d avoid all hardware RAID and go for the highest capacities that work in cheap enclosures that will simply put everything on three devices. Let some automated management software ensure it.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
In the two situations you presented in the beginning of the video the 4TB drive was a better option than the 6TB ones.
5 X 4TB drives = US$525.
12TB in a RAID6.
Or 16TB in a RAID5.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Since I know which ever I buy, I have to buy at least an additional one for back up, buying more smaller ones means buying even more or buying the big one for backup which would need a backup.Lol???? Fact is that I bought several 8 TB drives because they were a great price and serve my needs well.????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Since I know which ever I buy, I have to buy at least an additional one for back up, buying more smaller ones means buying even more or buying the big one for backup which would need a backup.Lol???? Fact is that I bought several 8 TB drives because they were a great price and serve my needs well.????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
hi, i’m from the future – HDDs are $10/TB now, so you might as well go big instead of holding a ton of small ones. your failure chance is about proportional to the number of drives you have anyways, so the risk cancels out if you copy-paste (RAID 1 equivalent) every once in a while to a copy
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I didnt understand a word you said when explaining shucking. Instead I had to look it up on Gemini.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The cost of having like a 6 or 8 bay nas and a bunch of smaller drives id rather get a 4 bay and populate with 12tb drives in paritiy, if one fails il just rebuild and im essentially big in the middle sweet spot of price/per tb and setup/storage capacity wise 4 bay makes the most sense.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Why don’t you link the calculator tool that you are using?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
which hard disc manufacturer is best ??? is it seagate ???
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
what’s a raid server ??? thanks
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The first comparison stacks 2x12tb(24tb) with 3x6tb(18tb) and call it a win in price for the latter? ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
“Yes”
There. I saved you all 19 very long minutes.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
You’ve earned my sub. I’ve run an unraid server for 14 years and have continually upgraded the hardware and drives. Your channel has great info, thank you.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Is this really relevant now with the price of SSD’s coming down? Could we have an update with M2 and Esata SSD’s?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I usually go for bigger drives because the cost of smaller drives is always much higher per TB, I generally look for a cost of 11-12 USD or 16-17 CAD per TB as a good value I paid about that for 2 18TB x18 EXOS drives One for my NAS and one for my Desktop/Workstation a few years back from server part deals before they raised the prices up so high it was not worth it anymore. I also do not need redundancy since the data on my DIY NAS is all just media on Jellyfin and some files I have backed up elsewhere. It’s also got a 500GB SSD cache just for good measure.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Right now I am buying off used 500GB HDDs off local market and building a 12 disk array. Works out quite cheap and enough supply is available to buy extra as spare. I am doing this not because I prefer 500GB but because the price is very cheap and available in plenty. I switch it on only twice in a week for taking backups, so small drives doesnt matter much.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The entire point of having a NAS is max porn storage so I’m going 28TB drives! YOLO
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Remember how processors became more powerful ? Not by increasing processing power per processor, but by increasing number of processors, I.E. cores. Same with the disks: more smaller disks, configured as RAID volumes, with redundancy and striping, managed by hardware accelerated controllers where required.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
As a sysadmin friend told me: it all comes down about price – think how much are you willing to pay in case your RAID goes down.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
A lot of hand waving about nothing. The best way to do it is start with a 4 bay or more NAS, and buying 2 of the largest drives you can afford. Run that in RAID 1 (mirroring) until you fill it up. Then add another matching sized drive and switch to RAID 5 or SHR, your space will double. Run that till you fill it up and add one more matching sized drive. Now you’re at max capacity of the array (for a 4 bay) and you fill that up. Then you either buy a NAS with more bays, or you start swapping drives out for larger drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’m new to this. I get how 2 18TB drives equals 1 18TB RAID. I don’t get how 4 6TB drives equal 1 18TB RAID. To me, that only makes sense as a 12 TB RAID. How can one 6 TB drive manage to play defense for 3 entire drives of the same size? Wouldn’t there have to be SOME data loss in the event of a drive failure? I’ve yet to see anything actually explain how this magic works.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
parity is for losers, YOLO
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Great video, one point missed is capacity / money spent. with some drives you get more per dollar spent then with others
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I think the obveous answer is more big hard drives. – last year I put together a 36 bay server chasis, currently with 3x 8 disk raidz2 vdevs (2 16tb and 1x 14tb), and I’ve got room for 1 more vdev worth of disks to expand.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Took a shot renewed right from WD. WD Elements 6TB $106.61 all in. Shucked. Red Plus NAS ! Went right in my Synology DS223.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
6TB HDD seems to be the sweet spot on sound cost and power use.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I personally prefer a few large capacity drives. Get a NAS with multiple bays and buy 2 or 3 16TB drives. When you need more storage buy another drive and add it to the pool. Drives also get cheaper over time.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Speed vs heat/noise/power consumption
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Like you may mention this yourself, but the funny thing is that if your building your own NAS ITX cases are actually more expensive, ITX motherboards are more expensive, so when building your own NAS is actually often the same price or cheaper to have the ability to have more drives, but that comes at the cost of the cases not being made to be compact so they do take up more space.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
To save everyone a lot of time: Here’s what chatGPT had to say about this :
More Drives vs. Bigger Disks for NAS
Factor More Drives Bigger Disks
Performance More drives = higher IOPS & throughput (RAID benefits) Fewer drives = less overall performance
Redundancy Better redundancy with RAID (e.g., RAID 5/6/10) Fewer drives = Higher risk of multiple failures
Capacity Growth Easier to expand by adding drives (if NAS supports it) Can be limiting unless you replace all drives
Power Usage More drives consume more power Fewer drives use less power
Cost Efficiency More small drives can be cost-effective at times Bigger drives may have a lower $/TB cost
Failure Risk More drives = higher chance of individual failures Fewer drives, but longer rebuild times if one fails
RAID Rebuild Time Faster rebuilds (especially in RAID 5/6) Longer rebuilds = higher risk of failure during recovery
General Recommendations:
If you prioritize performance & redundancy, go with more drives (e.g., RAID 10, RAID 6).
If you want higher capacity with fewer slots, use bigger disks.
If you have limited NAS bays, opt for the largest disks you can afford.
If your NAS supports ZFS (like TrueNAS), more drives help with redundancy and performance.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Big drives are good until you go full retard and use some 20tb drives then one fails and you wait week for array rebuild and in the meantime next fails
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Just shy of two minutes in, and already something needs addressing.
IronWolf drives are currently more expensive than the more capable Exos drives of the same capacity. Always check between NAS and enterprise versions of a particular brand before choosing, though don’t go with standard NAS for WD because of SMR (which I’m sure will be covered at a later point in this video).
I guess the main point is, when in doubt, look for enterprise versions of a drive first, then see if the NAS versions are cheaper. Then make sure those NAS versions don’t have some crippling drawback like SMR.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Many smaller drives in raid config require a more expensive NAS with more HDD slots and also uses more power than a couple of big HDDs. You can even run single large HDD 24/7 with scheduled rsync tasks to avoid using the second drive too much and extend it’s lifetime. In most home NAS cases you don’t need 24/7 access to the NAS, as it’s mostly there to provide media streaming when you’re free after work. And for this specific use case a couple of larger disks in raid1 or noraid with rsync makes more sense and helps to reduce electricity bills.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve been researching NAS for a while, and when I build one, it will be big.
For now, i have a single 20tb hdd, in a single bay enclosure.
I only put 4k video of which I have a low res back up, and once I’m ready to build the nas, ill transfer everything over.
I just have to cross my fingers between now and then 🙂
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
everything’s good until drive crashes, what is the best way to backup in 2024 on a measly budget?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’m looking at getting a DAS, I guess this info still applies
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Do you not have enterprise mechanical drives starting ~12tb that replace atmosphere with an inert gas that reduces sound, friction, and power?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
this is a pretty detailed overview of the advantages and disadvantages so everyone can make up their own mind
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More is faster and more reliable using a raid array with two drive redundancy
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I think you got most of it, what you maybe have not talked about is that if you use RAID 6 can you buy different drives at different times from different brands and over time slowly switching drive out as you see fit, you do never have to put the system offline, and you do never have to copy one large drive to a new one. In short, just feed a new HDD once in a while and the system will never go down.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Why do you say TB every time? Why don’t you just say terabyte like a normal person?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I started with 6 6TB. Wish I got larger drives. Cheaper per TB and more efficient. That said, I got dual parity for my important files and now 24TB drives for media that I can simply redownload.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have 2 wd gold 16TB drives mirrored and love them. Quiet and responsive. Wicked warranty too.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
+ point for smaller drives, if 1 fails out of warranty. its cheaper to replace and getting that raid going again.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Amazingly comprehensive research. Thank you!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Easy answer…more big hdd is good
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
so my solution after this video was: big and many. ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Virtualised NAS: 2 pools of 4Tb x3 with 60Gb RAM (read cache) + NVMe special device mirror (50Gb) for small blocks (<128k)
Prioritised sound so they are 5900 vs 7200rpm with rubber tray mounts
Checkout the Backblaze HDD failure rates (manufacturer, capacity) especially before believing the marketing for _Enterprise_ or _Pro_ drives
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
what if i get refurbished bigger drives
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The only proper solution is more hard drives that are bigger. I don’t want to put smaller hard drives because it just eats up space that a bigger hard drive can go into instead.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
No 1 NAS rule, use different suppliers, NEVER take 2 or 4 from the same brand
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Who ever had to copy a 8TB that made strange sounds, understands Einsteins relativity theory
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
A very informative video for sure.
I’m at the point where I am slowly upgrading my offline nas… my nas is a repurposed PC. It is a repurposed PC with space for 10 spinning rusts (with 5in adapters) and 4 2.5in drives.
And the kicker, is that it’s all sitting on windows storage spaces.
My problem is, I can not move to something like truenas or w/e because all my stuff is on storage spaces already. I do not have enough free space to do a local copy, and I couldn’t figure out how I could download from a cloud provider from truenas so I was kind of screwd and had to revert back to windows =(
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
great video, thanks.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Lots of good points for both sides but you didn’t answer the question:”Which is better?” Please make a video with the conclusion and thus the answer. If you don’t have an answer it is just clickbait and you should have chosen a different title.
That being said I liked thevideo.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
i have 2 slow ones. Is there any way to add faster ones but don’t make the whole system as slow as the 2 slow ones?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have HDD’s of various sizes. 2TB 4TB, 6TB, and 16TB.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
This video could have been five minutes…
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Another point to consider is when the inevitable drive failure happens…
How long does it take to rebuild the array?
My 12TB RAID5 array takes ~23 hours to parity check or rebuild a failed disk.
The bigger the disks, the longer the rebuild. If your bought a batch of disks from the same retailer at the same time (common thing to do)… will a 2nd disk fail during the rebuild?
So another tip – buy your disks from different retailers (2 from here, 2 from there kind of strategy)… hopefully you will get disks from different manufacturing lines or at least different batches to reduce the likelihood of simultaneous failures.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I would say more drives, more chances at redundancy and rpms somewhat combine with raid so the speed increases.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Thank you for this video sir! Good as always
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Based on a 6 or 8 bay Synology system, whats the best size drive for reliability in Seagate drives..?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have 20tb of games to clone and not sure which way to go lol
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Another specific advantage, related to the advantage of simultaneous reads & writes on multiple disks, is that you can tune a RDBMS so it purposely spreads data across multiple drives and even platters to optimize access, especially for searches.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Sadly I’m seeing this a year late. Anyway, I don’t think you hit reliability as might relate to density. I’ve wondered if an ultra-high-density drive can really and consistently have as few errors as lower-density drives, and if it is much more sensitive to movement and shock.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Dude your pool of teeth is degraded. You still have some redundancy but you need to add new teeth and resilver ASAP or you won’t be able to chew anymore.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
16tb drives is my sweet spot for storage to drive failure ratio
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Great video. One tip from lil ol me. First nas I ever used I bought 4 identical drives same make, model, style type. Unintended consequence was……. Same mtf. All the drives started failing close to each other. Next nas I made sure had a mix of different brands, different styles, mix of new and used. That should spread out the failures to different times
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More drives is always better. If you have one disk drive, failure of that one drive and you could loose everything. With more drives, you can run a raid array. With options for mirrors drives. Options to strip across drives for incredible speed. Or data protection using a drive for bit checking to ensure data stays intact. Just swap out the bad drive. And then the ultimate, use them all together. Speed, reliability. So many options. More is always better.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Also remember: an active raid is not a permanent backup solution, it’s a stop-gap. You should always do regular backups to an offline media as well. I suggest a raid 5/6 for active use and backups then a mirrored external for offline. backups.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Lol. More and bigger lol.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The “not all eggs in one basket” is a bad figure for RAID5. Speaking from probability of losing your data, using LESS drives is better. Let’s say the drive failure rate is 3% per year.
– 2×6 TB RAID1: probability of losing ALL data (2 drives fail same year) = 0.03 * 0.03 = 0.09% per year
– 4×2 TB RAID5: probability of losing ALL data (2 drives failure plus 3 drives failure plus 4 drives) = 0.518 % per year
so the RAID1 is A LOT safer BECAUSE it’s using a double safe basket instead of multiple baskets that are connected and ALL fail if 2+ fail
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve been playing with that RAID calculator while I listened to your analysis, and boy, now I do have a headache.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Great video!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Wd red are 5900 rpm until 6TB. They are much quieter. The 7200 rpm and above are noisier.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I prefer drives under 4TB as I find them to be more bulletproof. Bigger video and game files as well as AI models have caused me to now need large capacity drives. I been on a computer since DOS. My first PC had a 100MB IDE drive. I used that drive till IDE was fazed out and SATA became the standard. It never died nor slowed down. But it did sound like the Predator from the movie. I stopped using it cause IDE was just too slow. I am 40 years old and I have drives that I had when I was a teenager that still work fine today. The one that runs my pfSense is a 2.5 inch that has been in a laptop for about 6 years till it went in my Desktop for extra storage for about another 5 years and now runs my firewall. Its the only old drive I have that clicks. Been clicking for years now but will not die. But every singe 4TB or larger drive I get will need to be replaced at some point cause they are sensitive like lil girls.
Vibration or noise or impact or temps or looking at it too long will break it. I have spare large drives just in my closet. No small drives cause they just won’t stop. That 2.5 120GB has been in bumpy cars, dropped 100’s of times, bumped into, ran sitting upright, ran upside down, sideways, slanted, its older than some peoples children, and still clicks along. Its seen soo many video drivers, windows updates and PornHub. But 4TB and up…a loud noise might startle the thing and make it slap its forehead with the back of its hand as it faints. You gotta wake it back up in the controller. Shaking a grown man and he will most likely survive. Don’t do that with a baby. But HDD’s is different. You can shake the baby HDD’s but if you shake the big grown HDD’s they are dead dead dead. We are at a age now where files are big now so I am building out a server rack using large HDD’s not because I need a server rack but because the server rack needs a safe place to even be a server or NAS like Hollywood. PC’s are built different. They will save mkv’s and load steam in the streets of Brooklyn even after being dropped violently because a bee flew in your face and swatting at it and missing the bee made you smack the PC on to the ground. Them small capacity drives are built like 50 Cent
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
IME, few motherboards have more than 8 sata ports, and most around 4. It’s definitely a better idea to use the largest drives available. Also, I don’t trust these NAS. I take something with ECC RAM and put linux on it, currently btrfs raid-1 with triple redundancy. So it can lose up to 3 drives and not lose data. I trust the code and security updates from Debian way over those a NAS gets.
I play with datasets for AI, and have accumulated over 72 TB of data, half of which is probably not essential, but makes reproducibility easier.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Not really a fair comparison comparing 2 large drives in raid 1 vs 3 smaller drives in raid 5. The smaller drives should be raid 10.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
“I hate seagulls!” While pointing up was too funny
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Gr9 vid man! Appreciate you going thru all of the various different perspectives and angles of all of this info! My plan is 6 drives, raid 6, at least 2 systems, 1 system as backup, 1 system live, large format drives, not going to be cheap, but want the redundancy of raid and mirror, allowing up to 2 drive failures at one time. Most likely just Truenas scale at this point. Subbed and liked! Keep up the great work!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Things are even more interesting when looking at CEPH instead of a single NAS. Off course you need at least 3 servers and fast and dedicated network
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Wow man! ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Im still using the orginal drobo????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Is it possible to set up my NAS to copy over from a HDD to SSD and paste back on shutdown? Or just work in parallel with the SSD as a main refference and buffer stack any writes that the HDD can’t keep up. I preordered myself a 6bay + 2 m.2 Ugreen NAS. I worry that the biggest size SSDs are 8TB, but I could add two and have 16TB, somehow copy that to a HDD. And any less important data on normal HDDS
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
He’s math aint mathing you used 3 6TB’s when you need 4, 2 6TBs for 12TBs and need 2 6TBs for the extra 12TBs for redundancy.
So here’s the math you mess up on 1 6TB=158 1 12TB=258 right so 4 6TB=632 and 2 12TB=516 so you are spending 116$ more and I guess you didn’t see you have 1 lass drive when you’re doing this or YOU are trying to miss lead people on what you are doing here.
People double extra check you’re math when you are calculating.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
This isn’t strictly relevant to this specific video but I’m asking advice I’ve been given the task of assembling a moderately large NAS for a small company.
I’ve decided I am going to include cache but it’s the type to get I’m confused by.
It happens to be a Synology NAS I’ve gone for, and I noticed that specific types of M.2 Sara or nvme are recommended. It basically narrowed it down to WD Red, FireCuda 520 and Synolgy’s own 400 or 800Gb Nvme.
My initial reflex was that it was probably a good idea to go for Synology as it’s the same make as the enclosure but 400Gb of Synology SNV3410 Cache is about twice as expensive as 1Tb of WD Red nvme.
Why is this and is there anything that justifies this price difference?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
This is sort of a strange take imo… it isolates an issue that cannot really be isolated like that in reality. There are too many variables to take every factor in a generalistic way and have it be useful.
So in a way you have to establish a sort of brake point – above X cost the value of data isn’t enough to justify the cost of keeping it. What I mean is that in principle you should have a NAS by a different vendor using different drives in a different location, to your primary. Realistically most peoples data is not “worth” that kind of solution run privately. So the most important thing really is to determine what data is worth enough effort to really make sure it isn’t lost. Back that up across several solutions. Like USB sticks etc. The rest? Yolo 😉
If you want to mess with this stuff as a hobby, all the power to you, but do back the important stuff up some other way too. Preferably “off site” however you prefer to do that.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Toshiba 16TB drives have been cheap for some time. Now the weet spot seems 18TB, but ymmv
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Bigger drives are better. But if the data is important to you, the cheapest way (if it is not for professional needs), get the biggest drive vs price you need, and have an extra one as backup you dont use except for backup. Keep that backup away from power in some storage shelves or so. Hdd you dont use last very long. Had a drive from 10 years ago that I almost never used and put it in ‘cold’ storage, so unplugged in a shelves, and worked like a Sharm.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ll put this out there for anyone to answer – I contacted MSI to ask them and the reply was basically “No Idea – let us know how you get on”. I have an MSI Tomahawk Max II Mobo, running a 5600X and 32GB DDR4 3200mhz. Because I have a 4x Nvme 2TB boot, I only have 4 SATA drives available (I don’t bother with a DVD). I have added a 7 port USB 3.2 card. So I’m running about 72-76TB of drives. I want to expand that a lot. The internals are only 500GB – I want to take them to 18TB. Will my chipset support that? Even MSI said “Meh – Dunno”. Has anyone here done it? Its a very expensive experiment if it fails….
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
too long, waste of time and doesn’t answer the question
what is it better? 2 units of ssd 2T or 1 unit of SSD 4T?
of course when it comes to performance
and of course same brand and type, like sandisk ultra 3D
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I realize that bigger ‘pro’ drive would be more reliable, NAS class/designed to be better, that’s why their also more expensive to the identical desktop version… BUT to make these lager capacity cheaper, one way *would* be to make them in desktop class and loose that extra reliability you only pay on ‘pro’
Plus, to limit higher capacity to RED drives etc, manufactures get more money, and users don;t have a choice if its not there.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Per gig is cheap now-a-days. However, i don’t think i should admit i still use Barracuda desktop drives in my NAS…
Their cheap, compared to RED drives and IronWolf.. Besides,from past experiences, they ‘whine’ allot in idle mode… Could of just been bad drive, but i doubt. These were 4TB drives
Also, power-saving can make up the difference between buying big drives… The presumption your making is NAS’s are designed to be on all the time and active all the time, which is not always true. There is always going sections of ‘idle’, time, (particularly after midnight),. If you have Scheduled backups going on a QNAP, your gonna allow a few hour either way before the next starts to prevent possible increased failure. In that time space, the dives will spin down after 30 mins (usually) thus saving power. If you work that over a given year, that’s still a bit of energy saved right there.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
When I first got a NAS for mass storage I got a 4 bay NAS and filled it with 4TB drives, it was nearly full after 4 years and I upgraded the drives inside it with 4 10TB drives.
I back up the most important data off on the NAS over the movies.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Honestly I just have a bunch of 4tb red drives (every seagate I have ever bought failed within a year.. all of them..) My reasoning is its easier to replace a 4tb drive than an 18tb drive. Both in cost and in time. If I fail on a rebuild then I only loose 4tb of data. (I use unraid) I only backup what I can’t get back (pictures, home movies, etc. I can always re rip my dvds and such. 3-2-1 can get expensive otherwise. Especially with larger drives.
The little nas boxes seem pretty neat but frankly an old pc with an hba card is all you need. Buy unraid once (or use truenas, openmediavault, linux, whatever you prefer) works. I prefer unraid because of the way it works. Even if you fail on a rebuild you only loose whats on the failed drive. With raid you loose the whole pool. With nas boxes your upgrade path is kinda expensive. With other options you can just use your old pc when you upgrade.
My 2 cents worth. A lot of options. Depends on risk, time, and finances. Everyone’s mileage will vary.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I enjoyed this video very much! Very informative!!! What I would have like to see is a graph that shows where the flipping point is to decide on more or larger drives, including the NAS itself.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Well, if you follow technology you would know that ceramic glass memory has been proven to be a much smaller, cooler and vastly larger in size capability that the current SSD and HDDs. The Ceramic Memory Drives will be integrating over the next 5-10 years and the HDD will be as useless as the VHS and 8track tapes. So… no need to currently buy anything bigger than 200% of your needs, as you will be replacing them before you fill them.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
i went with 24 14tb refurbished drives for my nas
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
It depends. If your nas it is just for fileserver and a few clients go foe bigger disk. If youf nas contains db’s and lot of clients, better more disk..
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
8 20 Terabyte drives run in Raid in my new computer in a Themaltake case is where I am headed..
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
you start with saying smaller drives are cheaper, and while they are cheaper as singles, if I were to buy a skyhawk 4tb its 21.5 per tb, a 20tb is 17.2 per tb.
an exos is bigger disparity, in favor of larger drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The answer is simple: the best is to have lots of big drives!
Crib the storage perspective, of course, not the noise/power consumption.
Of course, with larger drives one should be very sure of the backups. And preferably use 2-disk redundancy to boot. It may be also result in higher ram usage.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
What if we go with a mixed approach? i.e. we get a large NAS, but start with as little large drives as we can and expand from there if necessary
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Select drives based on workload and never mix workloads.
If you’re recording surveillance 24/7 don’t mix that with other data. The surveillance activity is going to wear out drives faster. Putting other data into that mix is putting that data a risk.
So you might need bigger drives for surveillance and maybe smaller drives for your other stuff. Create separate arrays to separate the workloads and buy drives that make sense for each workload.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I like it hard and big.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
You talk about the possible more possible points of failure.. but you miss the big point with Raid 5 vs Raid 1… raid 1, if one drive dies.. you take it out.. order a new one.. re-raid it when you get it.. with raid 5.. when one fails.. you have to get another drive and rebuild it.. b ut while that is going on.. the entire raid is OFFLINE.. so I normally recommend.. if you RAID 5.. order a spare to minimize the downtime…
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
would be nice to compare RADIx vs throughput comparison to see in which case yo can utilize 1/2.5/5/10 Gbps….
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Here is how I do it: get the price divided by total capacity to get $/TB. That is the true cost of your storage. Then you can compare apple to apple on all of your drive options and pick the cheapest one.
Just note that there is a trade off. The more drives you have, the more power it is going to draw and the more points of failures there are in your system.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I wait for special CPU with lots of PCIe lanes and very little CPU power consumption. They would need a verys special design, so i guess i will have to wait forever before i can get a Raspberry Pie like system with 128 PCIe lanes (remember, they don’t need to be active all at once, but you can’t reconnect them dynamically as they are point to point, not a bus).
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I choose both!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Get as big as possible because they get full faster than you think and with small disks you run out of SATA-ports.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I feel like power consumption… isn’t a factor. You’re going to consume more power. You should expect that.
Also noise… isn’t a factor. HDDs make noise. If you don’t want noise, don’t get HDDs.
Here are my take-aways:
1. Don’t just get 2 drives. Because you’ll end up using one for parity only and waste the space you could use.
2. Get 4-5 smaller drives at once so you can benefit from the performance boost. This also ensures you can have more useable space over all.
Unless you have the cash to fill out 4-5 18TB drives in your NAS, just get smaller drives. Then you can have better performance and more redundancy.
If you didn’t want high power consumption and lots of noise, you shouldn’t be buying a NAS and filling it full of HDDs.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More small HDD is better, when you have many HDD bays. When you have HP Microserver with 4 HDD bays, you have to buy large HDD or additional microservers.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’d always lean towards getting a bigger NAS and smaller drives rather than bigger drives and smaller NAS. There’s more options in terms of backup and space options.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More hard drives or bigger hard drives?
**MORE BIGGER HARD DRIVES!**
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More. That was easy. 😉
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More. That was easy. 😉
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
You know what, I have been researching to having a solution for iCloud and Google One Drive because I am really struggling saving my image RAW files and videos. Then all on a sudden a photographer Tony Northrup brought the light of a NAS! I did not know what NAS is until couple of weeks ago! Then I started to do my own research and found you. I know you dont have smooth voice and attraction catching vocal gestures, but I find myself in you, I would want to express my research so that people can decide what’s best for them. I have found the same agony in you. You are like a tech big brother who wants to advice whats best for us instead biased brand marketing. I like your videos. Just wanted to pay my gratitude because I know, a small wish can boost up the moral energy a lot cause you have done so much research, night and day sleepless time. I know for the video but I know it’s for the people whom you want to help so desperately. Thank you so so much.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More bays: allows expansion, means you can postphone an upgrade. Clarifying your data increase is also important. Duplicate finder is alao a good way to save money here.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
since when does England use dollars? WTF?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More bigger HDs????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
My understanding is that shucked drives can have the problem of not powering up unless you insulate one of the copper fingers. Not always, but if you buy 5, one may need the insulation on the finger. That should have been a con. I love your stuff. You explain well.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
muchas gracias hermano!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
hdd hum is something that drives me mad, I can stand the ticking etc but the hum goes right through me and i can hear it from one end of the house to the other.
So for now I’m just doing manual backups and using local storage, no networking.( I really dont trust networking much when it comes to viruses etc ).
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Cheaper more drives but what about power consumption? More watts consumed or is the same? Let’s say will last 6 years and had to pay more electricity ⚡️ during those 6 years that also impact
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
HORRIBLE HEAD BEATING FOR 20 minutes?? No thanks.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Would it be a good idea to have the redundancy drive twice as big as the primary drive so that when the primary drive fills up, the redundancy drive can become the primary drive and then get another redundancy drive twice as big as the new primarry drive and the original primary drive can be put in another location for storage?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
What about both, more big harddisc X3
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Having not watched the video… both have their benefits and drawbacks.
Benefits:
More means higher throughput can be achieved and higher levels of redundancy can be gained making the setup more resilient when it comes to disk failure.
Bigger means less power draw, less vibrations and less potential heat, less physical space used and more capacity.
Drawbacks:
More disks is more power draw, more vibrations more heat production and more physical space used. With the added redundancy comes less capacity as the redundancy means disks are there just to cover the situation where one or potentially more disks fail protecting you from data loss in those cases.
Bigger disks means less options for redundancy as you have less individual disks, less theoretical throughput and often higher cost because even though the cost per GB drops the amount of GB’s per disk is significantly higher.
In the end it does not matter much which one you pick as long as you first take some time and think about what your goal is with the setup maximum redundancy and not to concerned about max capacity well more disks is better. Maximum capacity and not to concerned about the data’s longevity less big disks is the best option. If your chosen NAS enclosure allows for more disks than you are currently using then less but bigger might also be a good option as it will allow you to grow the storage capacity over time.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
“I hate seagulls” <— ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
“I hate seagulls” <— ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
OK Typed up a long post and then lost it all… So here is a short version.
Check the manufacturers HCL (hardware compatibility list) before buying drives. And if you don’t find a drive of the capacity you want then consider if it’s worth the risk. RAID controllers can be real finicky about drives.
You may feel SATA and SAS is mature tech and there should be no compatibility problems, but there are and there will be more. I’ve worked with (from memory) Adaptec, Areca, Raidcore, 3Ware and LSI. Sometimes the compatibility problems are blatantly obvious, but sometimes they are a creeping problem that takes time to develop, and they don’t get better with time. Sometimes a firmware upgrade of the drives or the controller can help, but there’s no guarantee that either is coming if you start out with incompatible hardware.
Also stress test the arrays before your start using them. Run every storage test you can think of on them, and then try some more. Check the RAID logs and take note of any warnings. You don’t want warnings! Not even the non critical kind. Make sure there’s as little vibrations as possible. Vibrations can play havoc with RAID arrays even if they are not strong enough to cause a head crash.
Also don’t use Shingled magnetic hard drives. They are a pain when used for RAID.
Temperature! A interesting paper published by a storage company probably a decade ago showed that the ideal running temp for HDD’s seems to be between 35 and 45 °C. Higher or lower temperatures showed increased failure rate. But don’t take this as gospel. However we do know that high temperatures are bad in general, and 40°C is a quite easy target for HDD’s.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I don’t have that much data, so I end up just refreshing 2.5″ hdd every few years, and use the surviving older one as redundancy backup. as time goes on, newer drive will be cheaper with more tb, so if I don’t need those 16tb at once right now, I can just buy 4, 5, 5, 6 over the years whenever I need one. Currently have 500gb, 750gb, 1tb (dead), 2tb, 4tb, 4tb, 5tb, 1tb sata ssd, 2tb nvme
Sure multiple points of failure, but at the same time it’s not all eggs in one basket. I did once have 1tb hdd when it was huge in 2009, backup all my files, then trip on the power cable, making the drive dead, with all the 1tb data I just sorted. So nowI list down list of file I have in an excel sheet in gdrive. so if one broke down, I know exactly what data it stored. Especially if I have 1 hdd for 1 tipe of stuff. that one is for x, this one for y, this one for z. so I won’t need to find z in x.
Personal use 20tb should be more than suffice. which is probably 4x5tb or 5×4 tb. 450-500 usd probably. All my photos from 2010 is only around 400gb jpg. and since current hdds are 4-5tb or so, yea I can manage to save more copies in more drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
This is one of the most stupid videos I have seen .. you can’t compare a mirrored pair at one point and then say a stripped set is cheaper .. pointless
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
If you have seriously important data don’t use a NAS use a SAN, lots of drives only generally gives a performance increase only for reading not writing, RAID on NAS devices usually has some restrictions based on implementation of the standards of the supplier vs on board raid provided by server manufacturers. NAS providers are great at vendor lock-in. Also make sure you buy drives compatible with the NAS as they don’t cover warranty issues otherwise. Generally pro series drives offer 5year warranty non pro are 2-3 years
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
huge enterprise drives can go 300mb/s sequential while a 4 or 6tb drive usually cant even hit 200mb/s especially if they’re 5400rpm so fewer disks can be as fast depending on the size difference. Also, the power use is substantial when using more disks. disk power usage can be more than the rest of the entire system combined when talking about 10+ disks
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
put external drive back into case, supported still good, hahahahahaa.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
why the hell would a drive be cheaper because it’s in an enclosure.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More mechanical parts are wearing down using smaller drives vs few less drives same as a car with three small gas engines vs one larger most likely one of three water pumps will fail before warranty
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
This is absolutely through and incredible information. You just saved me HOURS of research
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
clip starts after 1 minute intro. In 1 minute I explain the easy facts 😉
More drives: good for raid level 5 or higher. Where raid5 needs at least 3 disks. In case you need a specific raid level, you need the least amount of disks.
More drives: eventually more cache if you use drive cache. Depends on drives.
More drives: more performance if your controller is still not on its limit.
More drives: can increase performance, if the blocks you need are on different drives.
More TB: less power consumption compared to the same storage with more drives.
More TB: higher density = faster access (compared 1 disk with 1 disk, not the raid in summary)
More TB: overall costs could decrease (smaller NAS, maybe more TB per $$)
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I use 8 x 8tb as standard in my 8 bay nas’s, JBOD. Reason is, I use a 2nd and 3rd nas as backups, and if a drive fails I just copy the data onto its replacement, that way I just keep 1 nas running, otherwise 2 would be on all the time, I do a backup using goodsync once or twice a month, I tried synolgys drive sync, too automatic. I like the control of goodsync.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Very short version… go for more drives. More smaller drives usually work faster AND they make less noise. My advise would be never to buy drive bigger than 8TB, larger drives come with a big drawback of noise. Also using more smaller drives and a drive failes its cheaper to replace and faster to rebuild.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
As of this month(August 2022) it’s actually cheaper per gigabyte to buy high capacity drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
To what extent can you mix and match drives in something like a Synology, QNAP or Asustor system? I have only WD Reds because my original NAS was a WD. I was wondering whether I can use Seagates if one fails. I was also wondering a switch to a bigger drive would work. Say I have four 8TB drives and I replace one with a 12 or a 14. Does that work? What impact is it likely to have on performance?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I had a slightly different experience from what is expressed here, though I’m not casting any doubt on the validity of the information. I have a Nimbustor 4, populated with 4x8TB, for 24TB of storage.
I went for 8TB because, at the time, it represented the best bang-for-buck and gave me a total capacity (24TB in RAID 5) that I was unlikely to exceed for quite a while.
The NAS itself represented the best box I could justify. Being four bay, it also gave me the opportunity to spread my expenses over a longer period.
When I originally set it up, it had two drives in it. It was kind of noisy but no more than I expected. When I added a third drive, the noise and amount of disc access was much greater than it had been.
Recently I upgraded to 8GB of RAM and added a fourth drive. The first thing I noticed was that the overall noise is far less than it was with three drives and almost certainly lower than it was with two drives. In fact, it’s got to the point where I rarely hear it.
This probably won’t be most people’s experience but it seems to me that either by luck or design, I ended up in a sweet spot. I can’t explain it but I can hazard a guess that this is the kind of setup the designers envisioned…?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I think its worth including hot and cold spares into the discussion too
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I think its worth including hot and cold spares into the discussion too
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More bigger hard drives
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
can we mix different sizes of HD, like 12tb and add a few 4tbs? thank you
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I dont think we should only look at size vs number but also failure rate. I would rather go with a disk that doesn’t fail on me that often then the one i need to buy a new disk every few years and rebuild the RAID.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Instead of buying a simple 3 TB it’s much more fun to buy a bunch of 100 x 30 GB.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
If you have two large capacity drives and one of them fails…that’s a HUGE SLOG to replace in one hit. If you have lots of small drives and one fails it’s not going to hit you as hard when you suddenly have to get the replacement.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
currently my Media collection is currently under 3TB so I do not need a very big set up yet. Currently using 3 2TB reds in a raid 5. About to upgrade to 3 3TB drives in a raid 5 Then have a single 10TB HDD as a Back up.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Would not want one with Helium because it would eventually leak out then it will fail.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I say buy bigger drives, but don’t fill up your NAS day one, then you can more easily grow by adding drives as they become more affordable
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Both.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I just built my own NAS after going through a 2-bay NAS and then added a 4-bay NAS. I built one with 18 HDs and it is much more expandable. I am using UNRAID and it has been great so far. It is much faster and I have so much more capacity. When I need more, I will replace some of my 6 TB drives for 12 TB drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
one point , is when one of your drives will die , is easer and faster to recover one 4tb drive than a 12tb drive , and you don t lose all your data just lose a part of your data , and you can come up much easer with 70 euro than 300 when you get a surpize dive falure ,
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
What about the best of both worlds: lots of big drives?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
If you don’t need the speed consider using 5400 rpm drives. They are cheaper and tend to be more robust.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
At this point, I’ve settled on the EXOS drives going forward for the capacity, cache, price, and warranty.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Or, Dell T630 LFF server £350.
Used 2GB cache RAID controller £110
6x used 8TB HC520 drives, £70 each.
Needed a server as well as a lot of storage, so leaving out CPU & SSD upgrades.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
As an Arch Linux user, I was torn between buying an expensive (new) tiny RAID machine with 4 x new HDD’s or using an old (but free) monstrous 12 bay Supermicro server with 12 (free) smaller HDD’s.
Decided to go the Supermicro route. Have to admit, I’m way in above my head on this and have been dragging my feet for nearly two years now. In the end, I’ve decided that any form of RAID like setup is not for me. Don’t want to pay electricity (UK prices) on a server running 24/7. The beast can sit in the corner and be booted up once a week, whereupon I’ll do identical rsync (ext4) backups to two of the four nodes. Then following month do the same to the other two nodes. If I have a week when something of critical importance is created, I’ll rsync immediately. Also like the idea of each backup being completely isolated from the others.
I know my PC HDD will one day fail. However, given a choice between losing a few days of data or paying 24/7 electricity for RAID… I’m prepared to accept the former.
Thing is, I’ve never heard of anyone doing this with a four node machine, so maybe there’s a good reason not to. I like the idea of the sever being extremely heavy, as it’s less likely a drug addled thief would be able to move it, or even realize the drive bays are removable. Always thought those tiny RAID machines were too easy to tuck under your arm and walk away with. In fact, I might even bolt the thing down, as right now it sits on a table.
Could’ve gone with 4 x HDD’s and backing up via USB. However, that’s back to the hassle of pulling them out from a hiding place and connecting all those wires up. Plus, I’d need to buy large expensive HDD’s. Yep, I just like having four sets of backups.
Yes, fire/flood is a possibility, but still have a cloud backup for all essential documents. Like I said, I ain’t no expert or computer geek. Maybe it’s a daft thing to even consider doing…
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
In 2004 I had 9 Seagate hard drives fail in a 2 week period and they were sequential serial numbers. When I contacted them about a possible issue with that batch they spewed out the corporate boiler plate response saying that wasn’t the case and that their hard drives were of very high quality blah blah blah. I asked for new replacements rather than refurbished ones but they wouldn’t do that either. I’ve never sold another Seagate drive since. I doubt the few thousand drives I’ve sold over the years that weren’t Seagate are missed by them but I also never recommend Seagate because of their piss poor customer service.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The time to rebuild an array with 1 of several smaller failed drives verses the time it takes to rebuild an array with 1 of two large drives is important to me as a home user.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve had 7X 4TB Hitachi Ultrastar drives for my NAS since 2015, and still haven’t had one go bad on me. I’ve run it in both a RAID 6 and RAID 10 with a hot spare, and in both hardware and software (WSS) RAID modes, and recently bought another drive to make it 8 and did away with the hot spare, making it the storage for my backups. Still pretty reliable, but I wanted to replace it with SSDs. I’m a believer in minimum 6 drive arrays for NAS, for both performance and redundancy.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I built two TrueNAS (was FreeNAS) using six 4TB drives each (4+2 ZFS2), back in the days.
I’ve been considering upgrading to six 8TB drives (4+2), but have also been thinking about four 16TB drives (2+2) instead.
Both get me about the same usable space (~32TB). Note less than 2 parity drives is NOT an option.
I’ve been thinking about it for a long time, but haven’t reached a conclusion. It’s a tough choice.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Nice video. Thanks. R.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I ended up just getting UltraStar DC HC550 16TBs because it’s cheaper than buying Ext HDD and shucking them.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
IF I “HAVE TO” BUY A BRANDED NAS BOX, I’d spend my money on the biggest NAS with the max # of BAYS possible. Cuz you can always buy cheap smaller drives at first, but if you get a small NAS and used up all your bays from the begining it won’t grow more bays in the future and expanding more capacity means you have to discard your smaller drives, and that is a drive doing nothing loosing it’s value as redundancy.
The question of more hdd or Bigger hdd its a wrong question. Why? because the purpose of a hdd is to hold data. So data security always comes first.
Product like 2 bays NAS are pointless, you can achieve that with any old computer or laptop laying around your house, hook it up to you network and you have a raid 1 (minimum) NAS, the rest is just SOFTWARE, heck if you like Synology that much you can use XPenology which is a hacked version DSM 6.2 and the new DSM 7.0 that can be installed in any computer. And if you think well my old computer consume a lot of WATT to be an Always on NAS, then find out the socket of your motherboard and buy the most efficient CPU on ebay. Like, I have an old i7 90W cpu, then get an i5 35W chip for $20 and it will be almost as fast as the fastest Synology box.
Then what is the appropiate rule to build a NAS. It’s pretty simple actually… you build it with the capacity you’ll need. A good rule of thumb is aggregate all your current storage cap in your house and multiply by 2 (chances are it took you years to fill them up). Most people without NAS, they won’t reach 14TB.
And this is how data centers are built, they buy by capacity and not expandability.
Second thing you’ll need to do is calculate how many disk you are willing to distribuite those “14TB”, always remember the more the better, cuz you will have more redundancy.
In my case I would go for used SAS drives on ebay, for one they are all 100% enterprise drives, and are 1/2 the price of SATA drives with the same Capacity, but that also means you need to build your NAS with a SAS backplane and a SAS HBA in mind. ie I bought 3 Dells R730 XD with 24 2.5″ bays, 24 cores, 256Gb ram ECC and it includes 24x 2.5″ inch 600GB 10k rpm sas drives. For only $900 ea. I bet you can get waaaay lower price if you go for r620
Now you can also get a r730 same specs but with 12x 3.5″ bays, there is one that comes with 12x 3TBs SAS drives a total of 36TB for $1400. Synology 12 bays costs $3000 and it doesn’t come with disks. Booooo
If you go to ebay, you can see SAS 3TB goes for as low as $15 ea and buy in bulk I found a 5x 3TB for $30 total LOL. Oh! and it’s free return, couple years more 6TB will be at the same price point.
And almost forgot, you can switch to SATA drive when you like. Cuz SAS hba with SAS backplane can take SAS drives AND Sata drives. Unlike most Synology NAS only accept SATA drives.
Of course power consumption is a problem but it’s like $25/mo I would gladly pay (cancelled Netflix and Disney Plus LoL), cuz you are dealing with a real server not only you learn new skills, and all the parts are super cheap. And you can always expand your server capabilities. Synology is moving to 2.5Gb and 10Gb as PREMIUM stuff… heck I’ve been running 10Gb like a decade ago. I moved to 100Gbps, not long ago, that’s 10GB/s!!! The cards costs like $150 ea and the switch costs around $600 for 32x ports of 100Gps, yes 32 ports. I moved all my nvme to boost the server storage, and all my terminals are all diskless because booting from network is almost as fast as having a local Gen3 nvme, and not to mention all the VMs and Dockers you can run.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
What’s the best HardDrive for HomeUsers (for Data, Video, and Surveilance)? …maby a Seagate Exos x16 (with 14TB) in a QNAP Turbo Station TS-464 8GB …….what do you think?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I buy bunches of drives from broken computers. Dirt cheap, better for the environment and a failure doesn’t matter when you’re using RAID.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Noise is really a bummer for me now. I went from 4x3TB red to 3x8TB iron wolf, and the noise is more than double, and far more annoying in character. Heat and power also way higher. For next upgrade I want 14TB plus disks, and they are all horribly loud. I want high capacity, but low noise, low speed, low energy, since I can have multi TB of NVMe cache.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Very informative videos. You give info that is very relevant without beating around the bush. You make a good point about balancing out between the cost of NAS system and the actual storage. One option for anyone starting out could be to go for a smaller storage and then buy more/bigger HDD as the data grows and HDDs become more affordable in future, while investing in a NAS with more bays for future-proofing if really necessary. That also means hopefully sticking with the NAS with more bays for a longer time, given the initial cost.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
*Important* I am working on a master list of HDD/SSD Shucking! It currently covers well over 100 different USB Drives from WD and Seagate. If you want to find out which drive is inside your WD My Book, Seagate Backup Plus, WD My Cloud or WD My Passort, you can find it here. *Hard Drive and SSD Shucking, Master List of Which Drives Are Inside USB Drives* – https://nascompares.com/guide/hard-drive-and-ssd-shucking-master-list-of-which-drives-are-in-which-usb-drive-2023/
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Thanks mate for the great info. I have a 5 yr. old TS-653A with 5 WD60EFRX and I’m stuck with 1gbps connectivity. I’d like to get at least 2.5gbps upgrade so I’m going to get another NAS with faster networking and use it as a staging NAS. I’ll add a 6th drive to my 653A and move it to my in-laws house and work out syncing between the 2 NAS.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Nice Dreamcast sticker.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I think the mistake people make with NAS and especially raid5/6 is they think its a backup and its not. Any important data still needs a backup, RAID5/6 yes can increase read/write speeds but its really about redundancy (meaning uptime), businesses need to maintain uptime but not home PC users unless Home users are hosting web, file, plex servers for others offsite to access.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Today I tested positive for HSV after having a horrible outbreak , and feel the same way you described in your interview . Listening to you share your overcome experience gave me the glim of hope I needed to hear . I am glad that there are people like you out there who just want to help other people who are struggling with the same issues . Your words gave me the courage I needed to hear today to know that it’s ok . I can still be myself and now I’m enjoying my life the way I am supposed to . it is a blessing I came across you Dr Ofenmu YouTube channel
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Got to disagree, which is unusual on this site, the price difference is still massive. The drives near parity and generally drive companies I would never consider. Great video though in its research. Personally saved £1000’s even this year. (Excluding SSD’s). A lot of warrantees are completely worthless depending on the company and how they try to dodge the warranty they give. The interface issue is a great point, though still with skill by passable
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
For my 3.5 inch NAS drives I’ve been pretty happy with water panther’s refurbished drives rather than deal with the potential cons of shucking. I bought 8 12tb drives from them for $125 apiece when retail exos drives were closer to $300 and have a warranty.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Will Jack Daniels double down and push the rebranding of apple jacks to Adam’s apple jacks.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have adopted this rule now; Any HDD capacity less than 1.5x what you can get for $200 on the SSD side, is to be considered obsolete.
Currently you can get 4TB SSDs for just north of $200, that means 6TB (1.5 x 4) drives are now the smallest HDD that is worth getting. 6TB HDDs are now $90, while 4TB HDDs are $60. Up to each and everyone to put their cutoffs though!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Still not clear which is best ????????, so I bought a QNAP TS-1232PXU-RP-4G 12bay ($1475) and put in 12 x 20TB drives (Ironwolf Pro $329 each). After RAID 6 have 185TB available ????????2 x 10gbe, 2 x 2.5gbe network connection. Bought 13 drives to have a spare. Total cost before tax: $5752.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The performance of wd externals when shucked are terrible. It’s not even the spindle speed. Wd tweaks the firmware to automatically shave at least 30% read and write speed off automatically.
You can test this yourself. Start a large file transfer then do a smart test during the transfer. You will go from 180/200MB/s to over 250 for the duration of the transfer. What bothers me is these slow speeds are still at 7200rpm. So you get all of the noise and heat, but at a crappy speed.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
@NASCompares just letting you know the chapters for this video are mislabeled – when you hover over a section of the video the sections description is for a totally different video. Great video as always – thanks 😉
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The explanation was not clear at all, such needs to be unrushed and thought out.
BTW I have done it for decades. In recent years I shucked cheap M-SATA SSD cards on sale, putting them in a 2 5″ internal disk adapter enclosure to upgrade old out of warranty laptops which had slow laptop HDD system drives.
As a UNIX sysadmin in the 90’s there was a real temptation to upgrade disks in neat Sun SCSI enclosures with newer drives, they could go from 200MB to a whole GB of faster SCSI disk ????????
Those large IBM disks bought new had to be put in an enclosure anyway as they were sold for internal PC 3.5″ bays.
OTOH I have recently put another 1TB 2.5″ HDD laptop drive in a desktop rebuild of used parts, it’s intended to back an NVME cache as tiered storage for the forgotten cruft that accumulates under Windows in default folders.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I can’t bring myself to do it, any warranty is gone when tearing that enclosure apart. They own it for better or worse.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I think that my biggest shucking success was last year when I was informed by a friend that the storage company he now works for was about to dump a load of brand new external drives containing 4tb WD Red Plus drives into their online store as refurbished after a production line problem slightly scuffed the cases (it was apparently cheaper for them to flog the units off as refurbished, rather than pay people to re-case the batch). As such I was able to fill a new NAS for just over half the price it was originally going to cost me and get a few spares just in case.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
TLDR?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
A few years ago, I shucked LG branded 2.5 HDD and found that the internal Toshiba drive is not recognized by a Windows PC. It looks that the firmware doesn’t support SATA at all even it has a SATA port.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Don’t forget that some of these drives are not optimal for 24/7 NAS usage.
I shucked some WD drives and they had Ultrastar inside which I am using in my backup NAS, which powers on every few days to take a backup then shuts down on a schedule.
Picking those up on Black Friday for half the price of Red Pros or Ironwolf Pros more than outweighs the additional warranty buying NAS drives off the shelf.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have several Nas ranging from 5bay up to 12 bay all have shucked drives from 8TB – 18tb.
I saw on Amazon enterprise drives going cheap’ I read the reviews and buyers saying they had been used, but due to the very low cost for what there were I took a chance bought 3x 20tb turned up all looking new that was approx. 3yrs ago had no issues with any. I then bought 2 more a yr later, they had clearly been used but installed them no issues like new
Remember used enterprise HDD’s might have just been swapped out because a system error showed up or upgrade as a consumer normally your requirements are a lot less than in an enterprise, so you can still use these drives for years
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have a 10TB Seagate Backup Plus Hub external drive (purchased March 2020) that has a Seagate Barracuda Pro (which are now discontinued) inside. I also have two Seagate 1TB 2.5″ external drives and both have what Seagate calls their “Mobile HDD series” inside. The drives inside each are identical but one of them is limited to SATA 2 speeds, not that it really matters though for my use. This info was obtained from the Crystal Disk Info software so I assume it’s accurate.
I also have three old LaCie external hard drives from like pre-2010 I think and one of them had a 500GB Samsung drive inside and the other two had Seagate drives I think. Seagate of course acquired Samsung’s HDD business in 2011 and then acquired LaCie in 2014 I think. I also have a 2.5″ 500GB HGST hard drive that was taken from a launch PlayStation 4.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I was hopping you were gonna talk about NAS brands who are accepting shucked drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
WD artifically limit the speed to shucked 18TB’s in my experience. From 270MB to 210MB. I don’t shuck anymore for this reason.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have been shucking drives for years (You forgot the WD White label drives you find in the 12/14TB/16TB enclosures, apparently they’re relabelled Reds, in any case I’ve found them to be great, 7200RPM and I’ve yet to have one go “bad” on me. I have found Greens (slow), Red (Good), Blacks (Brilliant, I have a pair of 6TB Blacks that are 7 years old going strong in a spare NAS), but these days the best drives are the Toshiba enterprise 16TBs, Ok they’re a little noisy, but they work fantastically in a NAS box. There are apparently only 3 companies making mechanical drives in any case, they bought up all the minor companies, so your drives will be either Seagate, WD or Toshiba. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_defunct_hard_disk_manufacturers
And I’ve never had to do the “pin mod” mod yet.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
So basically you should avoid WD if possible because they’re shucking awful.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Shuck 2 Seagate 16tb usb enclosures which had the exos drives inside, I registered the drives and initially I got the 5 year warranty, checked back a year later and the warranty had expired ,Still work great after 2 years and used the original enclosure with 4td drives
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
This video is not sponsored by costa coffee. Pinky promise… ????????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Did that for a Upgrade from 2x8TB in RAID1 towards 3x8TB RAID5+Coldspare.
So far this worked out very well. Had looked out for quite some time but then decided on a WD-MyBookDuos. On those changing the drives is even Part of the Usermanual. That way you can use the external housing as it Was intended with other drives if you like.
Right now the shucked drive has over a year of running time in my qnap and i habe Zero issues. This drive is even 5-8 degrees cooler than the regular WD-Red.
Would Do it again. Saved a lot of money at the time of buying!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have three Synology NAS’s DS1821+, DS1621+, & DS920+ that have a total of 21 shucked drives including cold spares. Been running up to 2.5 years now with out a single glitch. This is the first time I tried it, but has worked well for me. Used 14 & 16TB drives from either WD Easystores or WD Elements. So, it’s been a positive experience thus far. And to your point I got the around Covid time, when everything was higher cost if not available at all.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Garn darn, Robbie. Awwww shucks ! Gday mate????????????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve done this 3 times in the past few years, all WD Elements from Amazon (2 8TBs and a 20TB). I had to do the ‘pin mod’ on all of them before my PCs would recognise them though. I’ve not had any problems with them so far, but I have kept all the packaging and enclosures just in case I need them for a warranty return. I always keep an eye out for special offers on Amazon for the Elements drives as it’s usually way cheaper than buying the bare drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I bought recently SanDisk G-Drive 12 TB and if anyone is wondering what is inside, let me know HC520 Ultrastar.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Keep them peeled, WD Elements Desktop Hard Drive 16TB was £ 183.24 on wd shop, why I did shucking a while ago…… will it ever get that cheap again?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
One vital point not mentioned, is that WD, I believe, in their Elements series of larger drives, does something to pin 2, I think, of their SATA rear connector such that it will not function when connected outside its enclosure.
If you can mask off pin 2, I believe it solves the problem, but the interface physically doesn’t look any different, but will not allow the drive to work as a bare drive without pin masking modifications that many cannot or will not do.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have a couple of shucked large capacity drives (WD) in my PC, but wouldn’t put one in my NAS devices. I keep the enclosures until the warranty on the external drive runs out in the hope of being able to put it back inside if a claim is necessary but I’m not sure how successful that would be. Not had to find out so far!
I’m currently dipping my toes into 10Gbe networking and ordered a suitable Intel X540-T2 NIC for the PC, and one NAS already has a 10Gbe connection so intend to run a cable (Cat7) directly between the two. I was looking for info on suitable switches to add later (QNAP QSW-M2108R-2C is favouritte ATM) but note you have not done any new vids on this subject for 10-12 months. So glad I found your channel it’s a goldmine of info and seems incredibly under-subscribed for the quality of content it provides.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Not sure if it’s still the case, but WD limited the drive capacities of SMR models to 6TB.
YMMV, but sticking to a minimum of 8TB usually avoids that one particular hurdle.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Price difference can be huge, I’ve shucked quite a few and price differences can easily be 30 to 60% or more cheaper. ie £330 for a bare drive or less than £200 for the equivalent capacity and identical performance.
Only downside is you can’t guarantee exactly what model you’ll get but more often than not on 12TB or larger drives you’ll get decent almost enterprise class drives for much less.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Interesting, thank you and good to learn about this topic, new to me. Opening the WD was also a nice demonstration of proper Oyster shucking. Cheers mate.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Thanks for this; I learned a lot
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
First! Omg I haven’t been able to do that since MySpace. Shuck em like there’s no tomorrow. If you’re in the states Black Friday is you’re friend. And yes, obviously it’s a gamble…hence the reason it’s cheaper. And when you shuck it…..Just look up the model number to find out exactly what kind of drive it is. CMR, helium filled, filled with hamsters on wheels. You can look that up.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I don’t buy Seagate – ever – crooks they are, different drives sold with the same SKU – some are from a modern Thailand factory, others are pieces of shit from an ancient Chinese plant…
Hitachi, Kioxia are decent companies, making excellent products
WD, well, Seagate bought them out – your mileage may vary, depending whatever they actually bother to ship you…
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
16, 18, 20, 22TB>>>>Talk about putting your eggs in 1 basket!!!
Sad this guy doesn’t even talk about the difference from smaller drives vs larger drives platter technology and the difference in drive life expectancy and likelihood of drive crash.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Smaller. Failed 2TB drive can take days to get the data back. Imagine the damage if you have to deal with big 12TB drive that failed. Don’t keep all your eggs in one basket. But if you can – get more and bigger drives. Spread the information around.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
RAID 10 with 4 hard drives seems like a good idea.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Answer is simple, more bigger hard drives
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
voltage is not equal to power consumption. watts is. you messed up the whole power comparison there. but i guess we get the point.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
26 minutes? Is there a short video where the question in the title is answered within 3 minutes?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More spindles, faster, faster rebuilds, etc.
My 12 spinning disk array does 5gb a second. Monster.
With enterprise hardware
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
he speed difference between more drives or not is one I have debater. I have an 1819+ and a newer 920+. The 920 CPU is about 50% faster, but the 1819+ had 6x HDDs, and i used the other 2 bays to run normal SATA SSDs as a RAID 0 cache, since the add on card for the 1819+ is really pricey for what it is. I ran PLEX on both and initially it felt like the 920+ was slower and stuttered more with larger files, however now there doesnt seem to be much of a difference. Hardly a scientific test but this is an interesting question. Not sure how to test it scientifically.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I like this video but it never answered the question posted in the title. It laid out a lot of considerations, which is helpful, but never came to a conclusion. I still do not know if it is better to get a 2, 3 or 5-bay NAS. Near as I can tell it is a wash.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
You missed one point. Kinda. It falls in line with the performance aspect. the larger the drive the longer the rebuild takes on a failed drive. So a 4 or 6TB drive, depending on how full the prior drive was may take 3-8 hours depending on the speed of your system / controller. But a 20TB drive could very well take 24+ hours which in turn leaves your array in a vulnerable state for a second failure. BTW this is why NO ONE should be using RAID5 anymore. The happy medium for me is somewhere between 10TB-16TB drives. They offer larger storage, but with a reasonable rebuild time.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
You REALLY don’t want to run raid 5 with just 3 drives. You risk data loss when rebuilding the array.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Another option is 8TB SSD drives. They are much faster, silent, don’t vibrate, use little power and are very reliable.
I’m not up on linux file systems or RAID wrt redundancy, but maybe 2 x 8TB and a 4 for error correcting, giving you 16? Just accept the risk given the greater reliability?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Binging your content!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Great information and I love the presentation. You are definitely not boring, even if some would say the subject isn’t the height of glamour. I bet you could be a stand up comedian too.
A lot of the useful stuff I have learned about NAS technology is from your videos. Nice one, thanks!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
It takes less time to rebuild the Raid with a smaller HDD. This would be an Argument for more smaller than fewer larger drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I just bought WD Gold 20TB. Crazy fast Built-in NAND and transfer speed up to 500MB/s !!! and much less noise !! I always love larger drive than small one. Because you will save money to throw away small HDD.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve deceided to get a NAS for home use as a media server. I’m checking out a lot of your videos to make up my mind what I actualy want and need, your videos are great, very detailed and very good explanations of the usage and for whom that particular NAS would be of interest. Kepp it up….
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
You don’t touch on the fact more drives you are using less data per drive at any write or read.
If you have 2 large mirrored drives, 100% of the data is processed through each of the drives. If you were to have the same capacity over 8 drives, the actual throughput is divided by 1/8th per drive. If you look at data loads of 300tb per year with an MTBF of 1,000,000 hours, the raid with 8 drives will last 8x longer.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
some of the bigger nas have addtional features as well that should come into determining the value proposition
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
You should do a video on having multiple drives, vs bigger drives, and the energy costs overall, in difference.
Energy costs factor alot into this too, especially today with electricity prices for people.
Your right to do such a vid to point this stuff out, but you could of shown the energy differences also.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve calculated how many GB you get per dollar and looks like the larger sizes give you a much better bang for your buck (14-18TB drives):
SG IW:
1TB – $35 – 29 GB/$
2TB – $65 – 31 GB/$
4TB – $105 – 38 GB/$
6TB – $158 – 38 GB/$
8TB – $177 – 45 GB/$
10TB – $224 – 45 GB/$
12TB – $258 – 47 GB/$
14TB – $271 – 52 GB/$
16TB – $309 – 52 GB/$
18TB – $389 – 46 GB/$
WD RED PRO:
4TB – $140 – 29 GB/$
6TB – $173 – 35 GB/$
8TB – $215 – 37 GB/$
10TB – $245 – 41 GB/$
12TB – $253 – 47 GB/$
14TB – $270 – 52 GB/$
16TB – $298 – 54 GB/$
18TB – $349 – 52 GB/$
20TB – $419 – 48 GB/$
22TB – $551 – 40 GB/$
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve been toying with getting an expansion unit for my 1019+ to get more drives or upgrading the current ones I have. 2 – 8 TB, 3 – 4 TB, 2 – 500 GB cache.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Actually, I think in most case It depends on how many IO is on your motherboard
such as, if you have 4 SATA ports and you used 2, then you will soon realize if you buy too many low-volume hard disks, you will soon be out of IO to let you upgrade in the future
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve got this idea recently.. In theory, what about using classic non-NAS type 2,5″ SATA SSD’s? For example four 2TB SSD’s in RAID 5? I know, it’s more expensive. But it’s silent, less power consumption and if I would have money for it? Just for home using, not really too much transfering data and important data will be backed up to external drive too. Is it there some statistics or something? What’s yours opinions guys? I have few data SSD’s in pc for long long time using by daily basis and they are immortal.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Wow, you really went into this one eh. I actually like the seagulls!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Maybe I’m on drugs or something because no one else is commenting on this, but in regards to the first segement “More HDDs Can Be Cheaper…”, your math seems all wrong. If a 18TB costs $389 and 3 6TB cost $158 each the total is $474. The 1 18TB drive is substantially cheaper. It seems to always be cheaper to buy 1 large drive than it is to buy 2 or more smaller drives to reach the same capacity. The one exception seems to be the 22TB RED drive. While its true that the TB per dollar increases the smaller the drive is, it doesn’t do so nearly fast enough to make buying multiple smaller drives worth it.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
For most home users, bottom-line .. use RAID 1. What you’re not telling the people is the difficulties in rebuilding a failed multi-disk RAID e.g. 5,6,10.
Multi-disk RAID 5,6,10,etc is when you need large storage capacities exceeding a single disk capacity. For example, large storage banks of video, photography, workgroups, etc.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More drives is more performance is quicker to spin down is less power used. More competent nas can run server tasks or wake on lan or….using less power in total than a smaller nas can in your total setup.
Large drives take to long to rebuild to be used in anything less then raid 6
I rather have more points of failure then 2 drives that are the same type and age and then pray for 24 hours that the remaining drive works to rebuild the raid 1 set.
And ofcourse raid isn’t backup, always make back ups because if it goes terrible wrong you can lose all your data no matter what setup you have. A fire or flood doesn’t care about your drive size.
If you don’t put the nas in a place where noise isn’t a problem, use SSD if you use your nas constantly or time it so the drives sleep during the day.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Thanks
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I too am a novice here, and found this incredibly helpful. Thanks so much for this from sunny Sheffield in the UK 🙂 I know you like QNAP, my Hi-Fi specialist suggest QNAP, but judging by security concerns from another of your videos QNAP v Synology, I had cancelled a 2 drive QNAP on Amazon, to rethink, and possibly have a 4 drive Synology. My Hi-fi specialist will only support if I bought a QNAP….. now that is very a difficult decision..!! Oh, and stop using big words.. lol.. ie, nebulous..!!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I just received two new WD Red drives from Amazon. Each had ENTIRELY different packaging and different stock numbers. Same size drives.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
the wd red pro and iron wolf are not enterprise drives. they are consumer nas rated drives. Ultrastars are Wd enterprise drives used to be Gold and Exos Drives are Seagates Enterprise hdd
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
It would clearly help to get a better grip of this topic and your conclusions, if you would visualize e.g. the performance, power consumption etc. of the different SSDs., This way everyone could easyly see the sweetspot of the price and the number of drives. We humans are visually predisposed ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’m back to simpler is better. Always did Synology Hybrid raid with 4 (Usually 4TB) drives. With my new 4 bay I decided on two Toshiba MG08 Series 16TB. I like it better.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Great video dude.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve talked about this on my channel more and more and I feel like its a fact that its still now as much known as it should be, I hate seaguls.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
It depends on what you need… More I/O – IOPS vs. need for more space. You can’t really get both… Great video! I have done a lot of videos on this very topic…
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
more disks = high power bill…
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
It is important to also consider rebuild and restore performance. With a larger number of drives running RAID 5 or 6 there is a significant difference in rebuild time compared to rebuilding a mirrored array. Also there is a difference yet again when you compare something like a RAID 10 to a pool of mirrors instead. In the case of RAID 5, 50, 6, 60 and 10 your backup will be of the entire array. In the event that data loss actually occurs and you must restore from backup you are talking about restoring the entire size of the array that was lost. However, when using pools instead you can elect to restore only the data from the underline RAID 1, 5 or 6 that you lost. These are all important factors to consider when selecting how you want to build out your storage array.
Also I should mention that if you are going with a lot of drives it is also possible to hybrid nest the arrays in such a way as to maximize performance while also minimizing your restore from backup time and risk of inaccessible data. For example you could take two drives and place them in a RAID 0 then take two more drives and place them in a different RAID 0. Then you take those two RAID 0 arrays and Mirror them together. You create sets of 4 drives in this method that you then pool together. The obvious con to this is that you would ideally add sets of 4 drives at a time to your pool.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The correct answer is more big hdds
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The biggest point you’ve missed is that the best way to shop us to first identify your risk tolerance, and then identify the workload needs, and buy either the largest drives you can afford that give you more redundancy than you think you, need or the fastest drives you can afford that give you more iops than you think you need. Your video also completely neglected iops, focusing on sequential io and capacity. Even just adding a small nvme mirrored cache device can turn a large disk pool into a virtualization and game storage powerhouse. Imagine what you could do with all-flash
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
If you are into data and/or storage then you can never have enough space.
Cheaper long term to buy the biggest NAS with biggest hdd’s, Otherwise you will run out of space and cost you more to replace all those smaller hdd’s or smaller NAS.
Not really worth it to buy the expansion unit only to fill it with more smaller drives.
Made that mistake with my first NAS, 5 bay and only filled it with 3x8TB (1 for redundancy) drives adding another 2 later on.
Thought I was being smart and saving money, Filled it after 3 years, I regret not going for 16TB drives at the start and would have lasted twice the time 6 or more years.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
After an almost critical incident, hot spare makes more sense to me. If not go for dual drive fail safety in synology to stay safe. Avoid buying drives from the same batch, I went as far as buying drives from different stores and different months.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I always tend towards the higher end of drive sizes but normally stay a step or 2 below largest capacity so I can have a better price per TB and just know that I can get bigger for cheaper in the future I prefer having expansion bays in my system open as my storage needs grow as that always have and will continue to
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
One idea to consider is the difference in power for say 4 big drives (say 14TB each with 1 parity) versus 12 small drives (say 4TB each with 2 parity).
The comparison of a small size storage ( smaller than 20 TB ) I think was the focus of the video and not larger size storage (35+ TB storage sizes.
Overall the video hit the points I think are important.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
More drives+ZFS=> Safer !
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Backing up 10 drives with several computers much faster. You also probably should not use 1 partition unless you want to wait 2 days to complete a back up.
I have heard many never make backups, so imagine the panicked person thinking his hard drive is failing, then waiting two days to see if the new drive got it all?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Q – More Hard Drives or BIGGER Hard Drives?
A – YES!
Always more and bigger, what can go wrong?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Thank you these great video’s, I highly appreciate them!
If I may ask a request on a video. using QNAP NAS and running Qumagie. How do you backup meta data from Qumagie as they are stored in an Qumagie database and not in the photo or on a separate file.
Ronny
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
The required amount of redundancy depends on how you plan to use the storage. If the NAS is the primary storage, then redundancy is very important. If the NAS is backing up primary storage on other computers, then RAID might be less critical for some people. The other consideration is point in time, or off-line, copies. If you have a fire or a ransomware attack, it might take out the whole NAS. Therefore, you need protected offline copies. That means maybe double or even more storage. How should we provide that? Does that remove the need for redundancy in the NAS?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Really interesting video, thanks. Here are a couple of ideas on presentation of the numbers: 1. Produce a line graph of price against drive size. That would make it clear that the price per terabyte drops a lot from 1TB to 20TB drives – $35 from to $21 per TB on pros. 2. Compare prices for some sample configurations with the same amount of usable storage.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Recently got an 8 bay QNAP, but getting disk combo nail is more challenging.
Current stack of drives don’t give me what I’m ideal after
3 x 3TB
4 x 4TB
2 x 12TB
Will prob get rid of the 3 and 12TB drives for more 4TB
The 12TB are HGST ultra star drives, as you say noisy too, but that’s not an issue.
Got 2 X 32Gb for cache
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
In the video you stated 5th of Jan 2022.. did you mean 2023 or is this a republish from last year?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
great content but your videos are just way to long on most subjects, could give the same info in a 10min video
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
This channel is so bad. Here in America I’m getting 12 TB Exos drives for $110 each, 6TB Hitachis are $45, and you can buy a motherboard, cpu, sas card, and a few drive cages for a lot less than the price of those pre-assembled and not expandable NAS cases
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
You were two weeks too late with this video, I just brought 5 16tb drives. I refuse to do the maths to see whether I made the right choice!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Appreciate your content but I do think you can benefit from shorter videos that get to the point a lot quicker. I find myself scanning and skipping through your videos a lot because I just don’t have half hour plus to dedicate to something, especially when I can Google and find an answer within 1 minute. Your content is mostly informational so getting to the point quicker is going to be much appreciated by everyone. Maybe start with the conclusion and then continue with the details as to how you reached your conclusion. ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Thks Mr HD 😉
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Get more drives, put it in your utility room, connected to your core switch, on a UPS.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I think the bit you didn’t really focus on when comparing two 18TB drives vs 5 smaller drives was you dropped from a RAID Mirror to a RAID Array. That is often a big performance drop. Also replacing & rebuilding a RAID 1 mirror is faster. And if you lose both, and want to pay someone to do disk plater recovery, the probability of retrieving usage data, drops significantly when they need to reconstruct the data off multiple drives.
When might you lose both RAID 1 drives simultaneously? Domestic: Voltage spike/lightning. Commercial: Some idiot unscrews the wrong thing & drops all disks on the floor.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Question is, why use HDDs anymore when NVMes are far better?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Unless I missed it, Price per TB is the biggest determiner for most people!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Why not “more bigger hard drives?” When I bought my NAS I got four of the biggest HDD I could at the time. Now they make drives that are almost twice as large, so I’m jonesing for an unneeded upgrade.
The noise is a legitimate concern, but I think for most people the best solution is to try and have a wiring closet / server room type setup and put it in there where you won’t really hear it. Of course, the problem with that is that the house basically needs wired for ethernet with a patch panel. I wish I had that.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Another excellent, and informative video! I actually looked to see if “Graham Malcolm…or whatever his name is”, entered a comment yet. He probably loves seagulls.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
There´s a interesting point to consider the multiple disk use. The SATA saturation (or other conector). If you are using the 10 Gb connector and/or VMs and docker applications.You can saturate the data bus with to much IO, exceding the SATA read/write capacity, and depending of biggest caches in SSD. And surprise, more probability of failure via hard/soft or energy. With multiple smaller disks more data can be read and write. The trick is what is the size of storage that you need and what size of NAS (slots) you have (including the extenders).
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’m just in the processes of putting together a NAS…SOOOOOO many questions and this was one of them ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
5th of January 2022? ????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Quality content ,love it
Currently got 8 PCS mg05 8TB which is super noisy when using in regular plastic Nas
Moved into a node 804 they are way less noisy on ticking .
Red 4TB non SMR is just fine, they are way silent compare to the mg05
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Agree head spinning. (5400?) My current problem is ripped blu rays will not stream via Plex over my network to fire TV. Having to convert down hard. Is it my network speed? (How do I test) is it my internet speed? (Max 33mbs).
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Ambient noise irrelevant
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Excellent question
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
As a novice, this makes my head spin. I’m thinking about a NAS to put all my video, music, and photos in one place, with backup, and if I can afford it, allow it to be cloud storage for my kids. I have 25TB of external drives, and while it’s good for storage (I’m afraid of disk failure and data loss). I’m totally lost as what to do.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Having just replaced or added HDD’s to both my 4 bay Synology and my 4 bay QNAP, my next NAS purchase to replace one of these will be an 8 bay. And I’ll install 3 larger HDD’s in RAID 5 or Synology Hybrid RAID and add new and larger drives as the need arises and prices fall. The worst thing about smaller NAS is the cost of pulling out perfect good, decent sized HDD’s because you need to replace them with larger drives. This is especially problematic with QNAP as you need to have all drives be the same size. With Synology’s SHR, drive sizes can be mixed ( although even that is not perfect). The extra cost of an 8 bay vs a 4 bay is easily saved by the ability to continue to use my older, smaller HDD’s. Don’t be deterred by up front costs; look at longer term use and future purchases and redundancies.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
If a drive in a RAID configuration fails, it takes longer to restore a large driver than a smallere. Thus it takes longer time before the redundancy is restored.
We are talking time in the order of days. During that period another disk failure leads to full data loss
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
If your Data is very very very important than use a 4 bay or larger, with larger Harddrives in Raid 1. in a 4 bay for example you have 3 Discs of failure.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I would have divided the presentation between Consumer needs/suggestions and business needs/suggestions:
in case of business you need IOPs and you do not care about noise because you have a datacenter (for small that it can be), so smaller disks in higher number give you better performance anche noise means Enterprse disks which have higher number of TB/year. at the same time as enterprise, for small that you can be, you should implement the 3-2-1 backup rules or at least having a backup site. the additional point is having a redundant power supply on your NAS.
for the remaining part, what you said is perfect for a consumer site.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Thank you for the thorough video! Perhaps one other aspect to consider is the best way to increase space with a 4-bay NAS that has expansion capability. I have a 918+ with 4x4TB. Shall I replace the drives with 4x8TB drives, or shall I daisy-chain a second 4-bay NAS with another array of 4x4TB?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
you showed us the pro iron wolf series why when the pricing does not match what you said
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I’ve mentioned this before, but if you are shopping for Pro drives, the only way to go is enterprise (Exos, Ultrastar). Depending on region they are much cheaper and also better.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I have an 8 bay DS1821 with 4x 8TB. The rationalisation was that as my data needs grew I could either add more 8TB or on the basis that over time costs would come down start adding say 12TBs and through SHR move to an all 12TB RAID.
So far so good.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Thanks Man! I know you since the days of my first NAS, a trusty old QNAP TS-269 Pro which is really a long time ago. And you are still passionate like day one about all things NAS and beyond, how is this even possible? Always great info, always on Top. Just Wow, yeah, just WOW and thanks for all the Seaguls. I would consider a video from you without “i hate seaguls” as beeing not authentic. yeah, i love this. ????All the best for 2023 and beyond! — Bernd
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
We all know you hate seagulls????
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Is Synology sponsoring your articles? Or pay you in any way?
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Can I use RAID at a software level (TrueNAS) with sata pcie expansion cards that are not RAID capable at a hardware level?
I’m building my very first NAS with a PC I’m retiring in a couple of months, and my motherboard does not have enough sata for the number of HDDs I want, there are a lot of sata pcie expansion cards on amazon but many of them say they are non RAID cards, so I’m not sure if I should buy them, if TrueNAS will be able to set the HDDs connected through that card in a RAID configuration.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Appreciate the mention that if you buy a number of the same drive from the same vendor you are likely to get drives from the same lot which if that lot has a problem means your risk for trouble is increased.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
In general, would it be better to go with a 2 Bay NAS with two 14TB WD Red Plus drives (larger capacity but still on the quieter side), or a 4 Bay with smaller drives? This is just for home use for storage and streaming videos.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
It would be really interesting to me if you could make videos at regular intervals for things like When will the price of hard drive come down and when will we see bigger capacities in the small classes.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Nice video!
I always calculate the price per TB. 😉
As that way there is often a HD-size (and above) that the price per TB is higher than the smaller/previous-size one. (price per TB)
We often opt for a wee bit smaller but more drives. As we always have 2x cold standby HD’s (thus unused!) near the NAS.
But more drives also means more power-use as you already indicated and also more heat. (more cooling might be needed)
Business-wide you should replace your HD’s every 3 years (5 years, max) but for the average user at home, you replace when really needed. (or after 10 years?)
To reduce risks, we also opt for multiple NAS. As a NAS may fail (power-supply, firmware-upgrade, bricking)
With larger drives the rebuilding of the RAID also may take longer., when something does go wrong.
BTW, also worth noting, the weight of the NAS might become significantly higher when you are using more drives (noticeable after 8x drives IMHO)
Generally speaking, the 6TB and lower are robusts as rocks (longevity), 8TB to 10TB are often the sweet-spot for pricing in my experiences.
Word of advice: buy as many drives as can fit in your NAS as down the line by the time you want to buy additional drives, the manufacturer may have moved-on to newer models..
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Fantastic comparison!
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
Factoring in that I had a stack of unused drives already, my first Synology was a 12 bay. I filled it with 1tb-6tb drives and was golden since that meant I didn’t need to buy drives until I needed more space(which happened, again and again ????)
REPLY ON YOUTUBE
I think it really depends where you are and what you can get. In some countries, it’s cheaper to get bigger drives and a two bay NAS, where other places, smaller hard drives and a four bay NAS ended up being the better option. I’ve always tackled it as a your-mileage-may-vary scenario.
Although if you want maximum capacity, a bigger NAS is the way to go.
REPLY ON YOUTUBE