I have discovered that a regular 4TB disk drive (with a 115MB/sec bandwidth for writes) needs almost 10 hours minimum for a RAID rebuild. By contrast, a 4TB Intel DC P3608 has a 3GB/sec sequential bandwidth, and its rebuild minimum time is 22 minutes. That’s 96.6 percent less than that for our 4TB HDD. The cost is significantly higher, but the time saved (not to mention other potential losses in 10 or more hours) is massively reduced. I’d like to hear your thoughts on this.
First of all, don’t worry about RAID rebuilding time. This is the main advantage of NAS and RAID, that drives can get broken, but despite that users can still access data and use other services. There might be a slight performance slowdown – if you have less than 6 drives in a RAID.
That is also true, that expensive PCI type SSD drives will rebuild much quicker. But these drives are not used for RAID systems. They serve as caching device for multiuser environments. They also can be used for tiered storage in Qnap servers (x82 series etc.).
If you want to increase NAS RAID rebuilding time, you have to get SATA SSD drives. Ass well as quick rebuilding, you will also benefit from massively increased input/output operations time. This is extremely useful when using a NAS as a database server, or web server, as well as virtual machine server. Increased IOPS will result in much quicker data transfer turnover.
If your budget is tight and SSD drives will not be an option, but you still need to increase IOPS because of apps mentioned above, you need to consider different drives.
SSD drives – Hight IOPS, High speed
NAS HDD PRO – 7200RPM slightly faster than regular HDD, but higher IOPS
Regular NAS HDD – regular speed 5900-7200RMP, regular IOPS
Fastest HDD/SSD based on IOPS
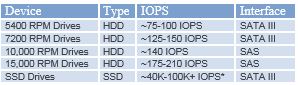
When do you need high IOPS drives:
- Random access
- Multiple clients concurrent access
- Database application
- VM access in a hyper-visor environment
- IP-SAN using block based data
When you don’t need IOPS:
- Sequential Access
- Video editing (Direct editing by using video editing software from a single work station)
- Video recording (Single client, e.g. from a IP camera or video recorder)
- Video streaming (Watching a video from the NAS)
- Large file transfer
- Data backup task
Need Advice on Data Storage from an Expert?
We want to keep the free advice on NASCompares FREE for as long as we can. Since this service started back in Jan '18, We have helped hundreds of users every month solve their storage woes, but we can only continue to do this with your support. So please do use links to Amazon Amazon UK on the articles when buying to provide advert revenue support or to donate/support the site below. Finally, for free advice about your setup, just leave a message in the comments below here at NASCompares.com and we will get back to you.
Finally, for free advice about your setup, just leave a message in the comments below here at NASCompares.com and we will get back to you.
 Need Help?
Where possible (and where appropriate) please provide as much information about your requirements, as then I can arrange the best answer and solution to your needs. Do not worry about your e-mail address being required, it will NOT be used in a mailing list and will NOT be used in any way other than to respond to your enquiry.
Need Help?
Where possible (and where appropriate) please provide as much information about your requirements, as then I can arrange the best answer and solution to your needs. Do not worry about your e-mail address being required, it will NOT be used in a mailing list and will NOT be used in any way other than to respond to your enquiry.
 Home: https://www.backblaze.com/cloud-backup.html#af9rgr
Business: https://www.backblaze.com/business-backup.html#af9rgr
Comparison with other service providers: https://www.backblaze.com/best-online-backup-service.html#af9rgr
Home: https://www.backblaze.com/cloud-backup.html#af9rgr
Business: https://www.backblaze.com/business-backup.html#af9rgr
Comparison with other service providers: https://www.backblaze.com/best-online-backup-service.html#af9rgr

